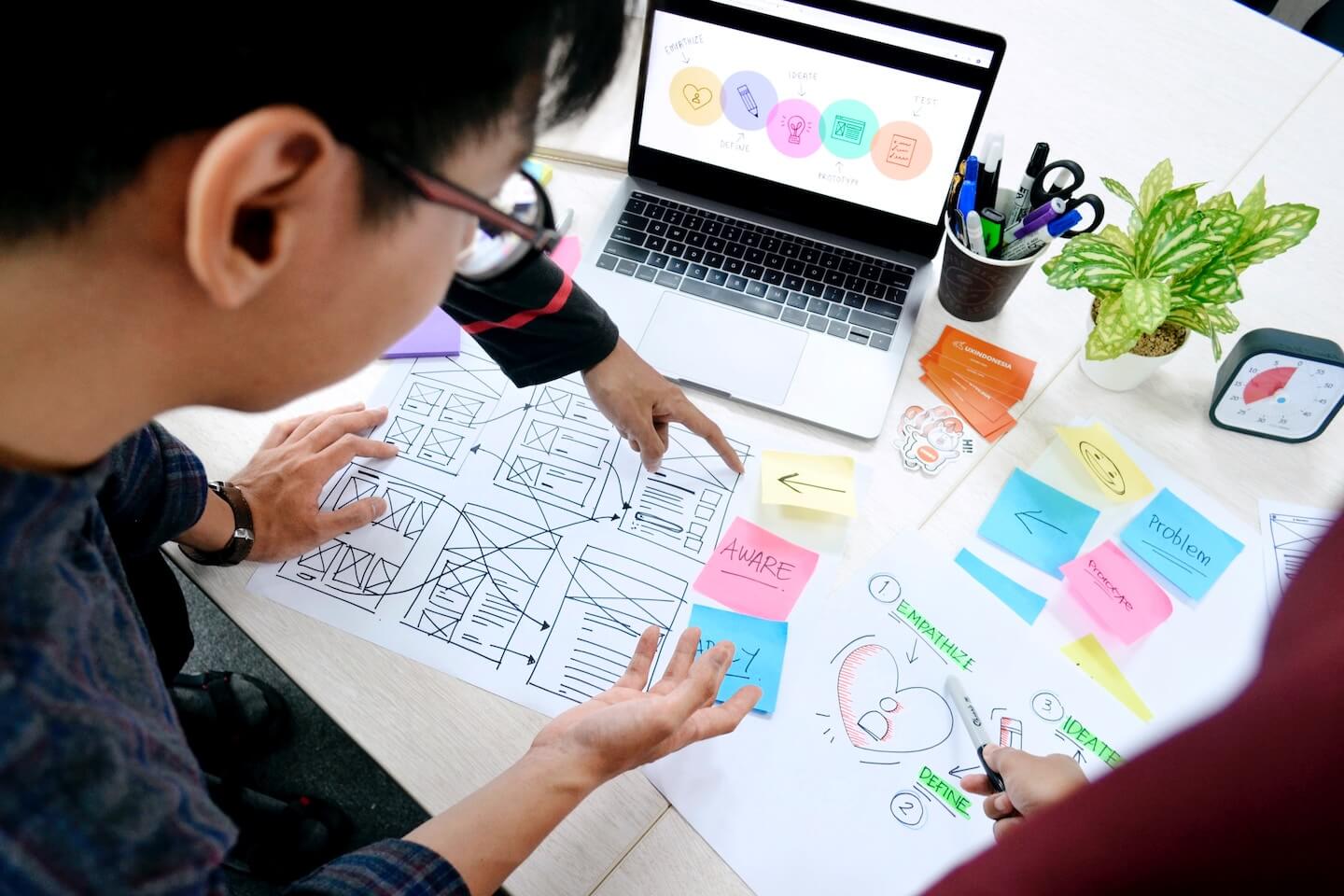
The world of project management is changing rapidly. Agile methodologies, especially Scrum, have emerged as transformative approaches that allow teams to adapt to change, generate value incrementally, and continuously improve. In today's fast-paced business environment, the ability to adopt Agile principles is no longer an option, but a necessity.
Our training courses were born from the need for a practical guide that goes beyond theory and explores the concrete application of Scrum. You'll not only learn fundamental concepts, but you'll also explore the nuances of implementing Scrum in a variety of team environments. From sprint planning to backlog management, each chapter is designed to provide an overview of the key roles, responsibilities, and practices that contribute to the success of Scrum projects.
For those preparing for Scrum certifications, this course also offers a dedicated section on how to effectively prepare, study, and pass certification exams. We'll detail the key concepts you need to understand and offer actionable strategies to ensure you're fully equipped for the certification process.
Whether you're new to Agile or an experienced practitioner, this course is a practical resource for applying Scrum to your projects, teams, and organizations. By the end of this journey, you will have a solid understanding of Scrum implementation, team dynamics, and the strategic importance of Scrum roles.
AGILE COLLABORATION
Agile collaboration is the cornerstone of modern project management because it allows teams to work effectively and adaptively in dynamic environments. Unlike traditional approaches that rely on rigid processes, Agile promotes flexibility, continuous feedback, and iterative development. It is designed to enable cross-functional teams to communicate effectively, make quick decisions, and generate value incrementally, ensuring customer satisfaction throughout the project lifecycle. Agile collaboration is based primarily on trust, transparency, and a shared understanding of goals. By fostering a culture of open communication and collective problem solving, teams can meet changing requirements without compromising quality.
Principles of Agile collaboration
Agile collaboration is based on a set of key principles that guide how teams interact and work together. These principles are designed to improve productivity, encourage innovation, and ensure that everyone involved stays aligned with project goals.
- People and interactions over processes and tools: Agile focuses on the importance of human interaction. Teams should focus on clear and meaningful communication rather than relying too heavily on tools and procedures.
- Functional software over comprehensive documentation: Agile teams prioritize providing functional solutions rather than getting bogged down in comprehensive documentation. This ensures that the product is continuously evolving based on feedback.
- Collaboration with the customer rather than negotiating contracts: Agile collaboration values active engagement with the customer. The project evolves through constant contributions and collaboration with stakeholders, allowing for quick adjustments.
- Responding to change rather than following a plan: flexibility is essential in Agile mode. Teams need to be ready to adapt their strategies and methods based on new information or changing requirements.
Communication techniques in an Agile environment
Effective communication is essential for Agile teams to collaborate effectively. Agile environments are changing rapidly and keeping everyone on the same page requires clear, concise, and open communication channels. Whether it's daily meetings or retrospective meetings, every team interaction aims to promote transparency, rapid feedback loops, and continuous improvement.
Agile teams often use multiple communication techniques to ensure smooth collaboration:
- Daily stand-up meetings: These brief daily meetings allow team members to share what they achieved the day before, what they plan to work on, and what obstacles they face.
- Sprint reviews and retrospectives: Sprint evaluations take place at the end of each sprint to present the work that has been done, while retrospectives allow the team to reflect on their performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Active stakeholder engagement: Agile teams maintain an ongoing dialogue with stakeholders, ensuring that any changes in project scope or priorities are addressed in real time.
- Feedback loops: continuous feedback, from both team members and customers, is essential for iterative development. This ensures that the product meets user needs and allows for rapid trajectory corrections.
- Collaboration tools: Tools like Slack, Jira, and Trello allow team members to share updates, track progress, and collaborate across sites.
By adhering to these principles and using effective communication techniques, Agile teams can maintain a high level of collaboration and ensure project success.
Agile project management tools
Agile project management tools play a crucial role in facilitating collaboration, tracking progress, and ensuring Agile principles are adhered to throughout the project lifecycle. These tools offer features that support fundamental aspects of Agile, such as sprint planning, backlog management, and real-time reporting. By using Agile tools, teams can effectively visualize tasks, prioritize work, and maintain transparency at all stages of the project.
Jira, one of the most popular Agile tools, provides teams with a platform to manage tasks, sprints, and releases. It allows workflows to be customized, making them adaptable to different types of projects. Teams can create user stories, assign tasks, and track progress on a visual board, ensuring everyone stays aligned with project goals.
Trello is another widely used Agile tool that is known for its simplicity and flexibility. It uses boards, lists, and maps to organize tasks and workflows, making it easy for teams to visualize work in progress. Trello is especially useful for small teams that need a lightweight, intuitive tool to manage tasks.
Asana and Monday.com are also popular project management platforms that support Agile methodologies. They offer features for task assignment, deadline tracking, and collaborative planning. These tools help Agile teams stay organized, ensure accountability, and facilitate smooth communication between team members.
By taking advantage of Agile tools, teams can not only maintain efficiency, but also increase their ability to adapt quickly to change, stay connected, and ensure transparency in their workflows.
Methods to improve collaboration
Collaboration is critical to the success of Agile, but it requires ongoing efforts to create an environment where team members can work together effectively. Teams can adopt multiple methods to improve collaboration, ensuring that all members are engaged, aligned, and working toward the same goals.
Foster a culture of open communication: Open communication is the foundation for strong collaboration. Teams should feel comfortable sharing ideas, asking questions, and providing feedback without fear of judgment. Agile teams have a vested interest in creating an environment where transparency and honest dialogue are encouraged. This allows problems to be resolved quickly and misunderstandings to be avoided.
Encourage cross-functional teams: Agility is about cross-functional teams where each member brings a unique set of skills. Encouraging team members from different areas (e.g. development, design, testing) to collaborate ensures that the team can address all aspects of a project. Cross-functional collaboration reduces silos and accelerates problem resolution.
Implement regular retrospectives: Regular retrospectives are a powerful tool for improving collaboration. They allow teams to reflect on what went well, what didn't go well, and how they can improve in future sprints. This promotes a culture of continuous improvement and ensures that team dynamics are always evaluated and adjusted where necessary.
Use collaboration tools: In today's digital workplace, teams often need to collaborate across time zones and locations. Tools like Slack, Zoom, and Microsoft Teams allow for real-time communication, while platforms like Miro allow teams to think and collaborate on visual projects. These tools help bridge the gap between team members working remotely and ensure everyone stays connected.
Building trust within the team: Trust is essential for effective collaboration. When team members trust each other, they are more likely to communicate openly, share ideas, and provide constructive feedback. Teams should invest in building trust by encouraging mutual respect, understanding, and support among members.
By using these methods, Agile teams can improve their collaboration, which in turn improves efficiency, innovation, and project outcomes.
SCRUM IMPLEMENTATION
Scrum basics
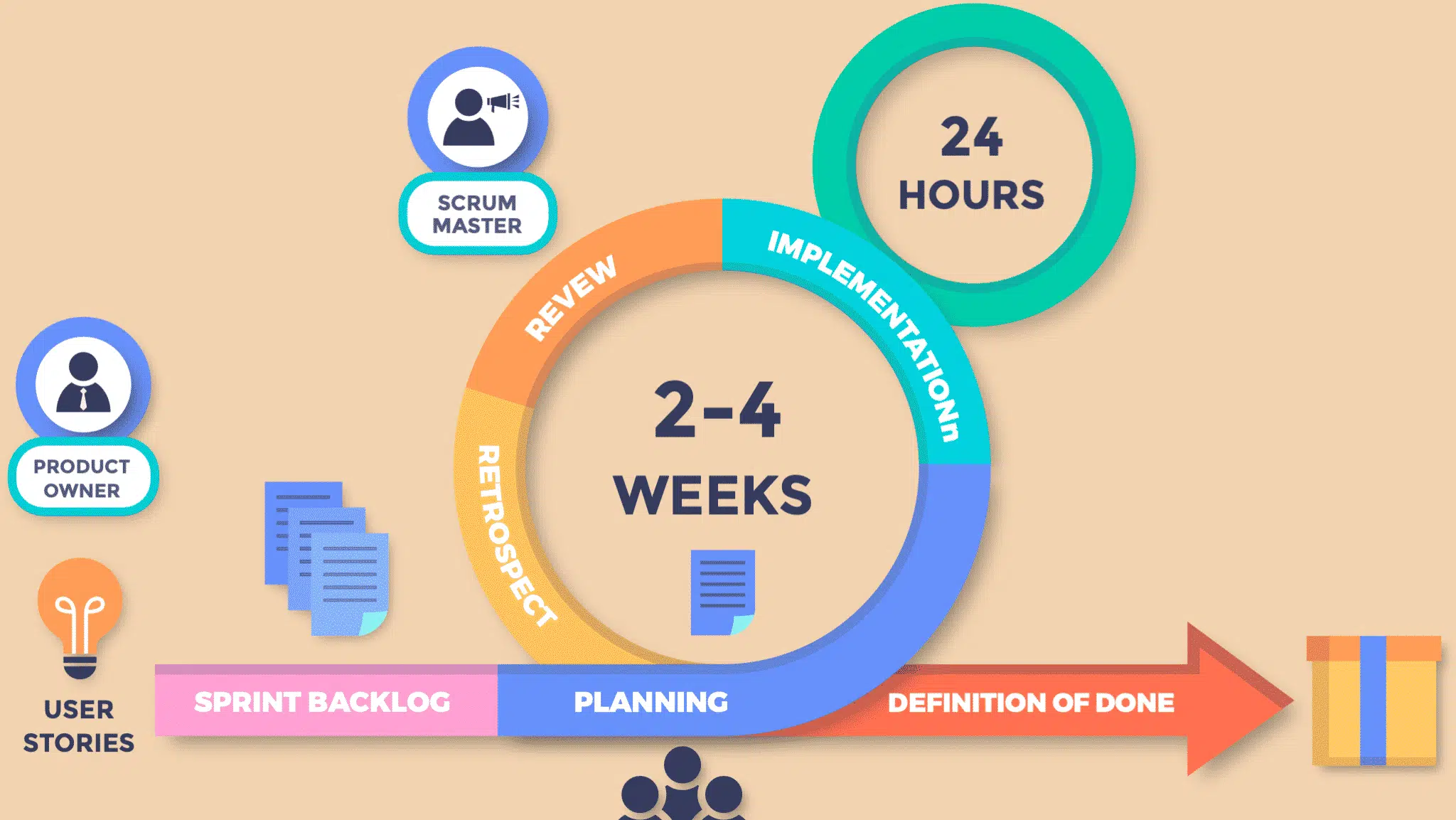
Scrum is an Agile framework designed to help teams work more effectively by breaking complex projects into smaller, manageable tasks. It is based on iterative and incremental development, in which work is done in cycles called sprints, which generally last between 1 and 4 weeks. The goal of Scrum is to provide the highest possible value by prioritizing and continuously adjusting the scope of the project, focusing on customer feedback, and accelerating development.
Scrum is based on a few key roles:
- Product Owner: Responsible for defining the vision of the product and for prioritizing tasks in the product book.
- Scrum Master: Ensures that the team adheres to Scrum practices, facilitates meetings, and removes any obstacles that may hinder progress.
- Development team: a cross-functional group responsible for getting work done, including design, coding, and testing.
At the heart of Scrum is the Product Backlog, a prioritized list of tasks or features to be performed. The development team executes these tasks during the sprints, providing product increments, which are reviewed at the end of each sprint.
Sprint planning and execution
Sprint planning is a key Scrum event where the development team, Product Owner, and Scrum Master come together to decide what backlog items will be addressed in the next sprint. The aim is to select tasks that can be completed realistically within the time frame set by the sprint, and this selection is based on both the team's capacity and the priority of the tasks.
When planning a sprint, two main questions are addressed:
- What can we get during this sprint?
- How will the work be done?
The team defines the sprint goal, a clear sprint goal, and identifies backlog tasks that align with that goal. After planning, the execution phase begins, during which the development team works collaboratively to complete the selected tasks. Throughout the sprint, daily meetings ensure that progress is on track and that any obstacles are identified and resolved quickly.
At the end of the sprint, the team organizes a sprint review to present the work done and gather feedback from stakeholders. This is followed by a sprint retrospective, during which the team reflects on the sprint process and identifies areas for improvement.
Managing tasks and priorities
Effective task management is essential in Scrum to ensure that the team stays focused and delivers value consistently. The Product Owner plays a crucial role in managing tasks by constantly refining and prioritizing the product backlog. The items at the top of the backlog are considered to be priority and are generally better defined, while the lowest priority items may still require further clarification.
During a sprint, the development team manages tasks through a Sprint Backlog, which includes tasks selected for the sprint. Teams often use visual tools like Kanban boards or task boards to track the progress of tasks, moving them into columns like “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.”
Scrum encourages the frequent reassessment of priorities. As new information comes to light or customer feedback is received, the Product Owner can adjust the product backlog, reprioritizing tasks for future sprints. This approach ensures that the team is always working on the most important tasks and can respond quickly to changing requirements.
Monitoring and continuous improvement
Scrum promotes continuous monitoring and improvement through a variety of events and practices. Daily meetings provide a space for team members to keep up to date on their progress, discuss potential challenges, and align their work with the day. These short, focused meetings help maintain transparency and ensure that issues are resolved before they become significant obstacles.
At the end of each sprint, the sprint retrospective plays a critical role in continuous improvement. During this meeting, the team reflects on what went well, what could be improved, and what steps could be taken to improve future sprints. This process of thinking and adapting allows Scrum teams to improve their processes, work more effectively, and achieve better results over time.
In addition, the Sprint Review allows for regular feedback from stakeholders, ensuring that the product evolves in line with customer needs and expectations. This iterative process of delivery, review, and improvement ensures not only high-quality work, but also the strengthening and cohesiveness of the team at each sprint.
ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF A Scrum MASTER
Scrum Master roles
The Scrum Master plays a crucial role in facilitating the successful implementation of Scrum practices within a team. Unlike traditional project managers, Scrum Masters are not responsible for leading team work or making high-level decisions. Instead, they act as facilitators, helping the team adhere to Scrum principles and practices while ensuring that obstacles are removed so the team can focus on creating value.
One of the main roles of the Scrum Master is to act as a leader in the service of the development team. This includes prioritizing the needs of the team, fostering collaboration, and ensuring that the team has the tools and environment they need to succeed. The Scrum Master also acts as a coach, guiding the team through the process of adopting Agile practices and supporting continuous improvement within the team.
Additionally, the Scrum Master acts as a mediator by managing interactions between the development team and the Product Owner, as well as between the team and other stakeholders. They ensure that communication runs smoothly and that everyone is in sync with the goals of the project. Finally, Scrum Masters act as change agents within the organization, advocating for the wider adoption of Agile principles and helping the organization adopt a more collaborative and adaptive way of working.
Key responsibilities
The main responsibilities of the Scrum Master are to ensure that the Scrum framework is understood and followed by the entire team. These responsibilities include:
- Facilitating Scrum Events: Scrum Masters are responsible for organizing and facilitating key Scrum events such as sprint planning, daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and sprint retrospectives. They ensure that these events are productive and that team members stay focused on the agenda.
- Remove obstacles: One of the most important responsibilities of a Scrum Master is to remove any obstacles that may hinder the team's progress. This can range from resolving conflicts within the team to resolving organizational issues that slow development.
- Coaching the team: Scrum Masters provide advice to the team on how to effectively implement Scrum practices. This may involve coaching new team members, providing advice on collaboration techniques, and helping the team understand Agile values and principles.
- Promote collaboration and communication: The Scrum Master ensures clear and open communication between all team members, including the Product Owner and stakeholders. They encourage team collaboration and create an environment where team members feel empowered to share ideas and work together effectively.
- Protect the team from distractions: Scrum Masters act as a shield for the development team, protecting them from external pressures or distractions that can affect productivity. This allows the team to focus on completing the tasks set for each sprint.
- Support the Product Owner: While the Product Owner is responsible for managing the product backlog, the Scrum Master ensures that the backlog is well-organized, clear, and prioritized. They help the Product Owner prepare sprint planning and ensure that the team understands the scope and goals of the tasks they are working on.
- Ensure continuous improvement: Through sprint retrospectives and continuous feedback, Scrum Masters encourage the team to reflect on their performance and look for opportunities for improvement. They facilitate discussions about how to work more effectively and make adjustments that will lead to better results in future sprints.
By focusing on these responsibilities, the Scrum Master plays a critical role in the success of the team and in ensuring that Scrum practices are applied effectively throughout the project.
Facilitation techniques
Facilitation is one of the core functions of a Scrum Master, as it ensures that Scrum events and team collaboration are both productive and effective. Effective facilitation techniques help the Scrum Master guide discussions, focus meetings, and encourage everyone on the team to contribute ideas. One of the techniques commonly used is active listening, in which the Scrum Master listens attentively to team members, clarifies points, and ensures that everyone's voice is heard. This technique helps uncover hidden problems and promotes open communication.
Another useful technique is timeboxing, where Scrum events are limited to a set amount of time in order to keep discussions on track and to prevent meetings from dragging on unnecessarily. This ensures that daily stand-ups, sprint planning, and retrospectives remain focused and useful. Scrum Masters also use open-ended questions during facilitation to encourage deeper thinking and exploration of ideas. Ask questions like “What could we improve on the next sprint?” encourages team members to reflect and provide valuable information for continuous improvement.
Group decision-making techniques such as point voting or five-handed voting can be used when the team needs to prioritize tasks or make quick decisions. These techniques allow everyone to express their opinions in a structured way, thus helping the team to reach consensus in an effective way. Finally, Scrum Masters often use visual aids such as Kanban boards or sticky notes to help teams track the progress of their work and ensure transparency throughout the sprint.
Tools and resources
Scrum Masters rely on a range of tools and resources to support their teams and effectively manage the Scrum process. Collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams are critical to ensuring open lines of communication, especially within distributed teams. These platforms enable real-time messaging, file sharing, and rapid decision-making, making them invaluable for daily interactions.
For task management, tools like Jira, Trello, and Monday.com help Scrum teams visualize their workflow, manage backlogs, and track the progress of tasks throughout each sprint. These tools typically include customizable tables or lists that reflect the various stages of work, such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” They provide clarity and transparency, ensuring that everyone on the team can see what tasks are being performed and who is responsible for them.
Additionally, retrospective tools like FunRetro or Miro can be used to facilitate sprint retrospectives, allowing team members to provide feedback in a structured and engaging manner. These tools offer interactive whiteboards where the team can document what went well, what could be improved, and action points for the next sprint.
Finally, Scrum Masters can access a variety of educational resources, including books, online courses, and certification programs, to increase their knowledge of Agile and Scrum practices. Resources like the Scrum Guide or platforms like Scrum.org and LinkedIn Learning offer tutorials, templates, and best practices that Scrum Masters can use to continuously refine their facilitation skills and Scrum management techniques.
ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF A Product Owner
Product Owner Roles
The Product Owner plays a central role in Agile projects, acting as the link between the development team and business stakeholders. Their main responsibility is to ensure that the team is always working on the most useful features, effectively managing the product backlog. Unlike traditional project managers, the Product Owner is not responsible for managing the team's daily activities, but instead focuses on the “what,” meaning what the team should develop next based on customer and business needs.
The Product Owner is the voice of the customer and ensures that the product provides maximum value. They work closely with stakeholders, customers, and end users to understand their needs and translate them into user stories and tasks for the development team. As such, the Product Owner alone is entitled to decide which features or functionalities should be prioritized for development.
Another key role of the Product Owner is to continuously review and refine the backlog, ensuring that the most important work is always visible and ready for the team. They should be available to the team to provide clarification, answer questions, and make quick decisions during the sprint to ensure that work runs smoothly.
Key responsibilities
- Product vision definition: The product owner is responsible for articulating the vision and goals of the product. They ensure that every task the team works on is aligned with overall business goals and meets customer needs.
- Product Backlog Management: One of the most important responsibilities of a Product Owner is to manage the product backlog. This includes adding, prioritizing, and deleting tasks to reflect changing project and client needs. The order book should always be up to date and prioritized based on business value.
- Prioritize the work of the development team: The product manager ensures that the development team is always working on the highest priority tasks. They need to consider factors like business value, risks, customer feedback, and timelines when prioritizing features.
- Stakeholder communication: The product manager is the main point of contact for stakeholders, keeping them updated on progress, changing priorities, and challenges the team may face. This ensures that expectations are aligned and that the product evolves to meet business goals.
- Collaboration with the Scrum Team: The Product Owner works closely with the Scrum Master and the Development Team to ensure that the team has everything they need to be productive. They participate in sprint planning, daily meetings, sprint evaluations, and retrospectives, providing ongoing feedback and support.
- Maximizing product value: One of the main responsibilities of the Product Owner is to ensure that the product offers the maximum possible value. This involves making decisions about scope, balancing competing priorities, and adjusting the product roadmap based on customer and market feedback.
Backlog management techniques
Effective backlog management is critical to the success of any Agile project. The Product Owner uses several techniques to ensure that the backlog is well-organized and aligned with the goals of the product:
- User Story Mapping: This technique consists in organizing user stories in a way that reflects the user's journey through the product. It visualizes the product from the customer's perspective and ensures that features are integrated in a logical and incremental order.
- Prioritization in Moscow: This method helps product managers categorize pending items into four categories: essential, should have, could have, and didn't have. This approach helps manage the scope and ensure that the team is focused on providing the most critical functionalities.
- INVEST criteria for user testimonials: The INVEST model ensures that each item in the order book is independent, negotiable, valuable, estimable, small, and testable. Using this approach helps the Product Owner create user stories that are actionable and easy for the development team to build.
- Backlog refinement: Regular backlog refinement meetings allow the Product Owner to review and update the backlog, ensuring that upcoming tasks are clearly defined and prioritized. These meetings help the team better plan for upcoming sprints and eliminate confusion during the sprint.
- Prioritization by business value: This technique consists in assigning business value to each item in the backlog. The items that offer the greatest value to the business or customer are prioritized over the lower-value features, ensuring that the team always gets the maximum impact.
Tools and resources
Product Owners can take advantage of a variety of tools and resources to effectively manage their responsibilities. Jira, Trello, and Monday.com are popular project management tools that allow Product Owners to create, prioritize, and track user stories, tasks, and epics. These tools provide visibility into the product backlog and help Product Owners collaborate with the development team and stakeholders.
Confluence is a powerful documentation management tool where the Product Owner can store requirements, customer feedback, and project updates. This tool allows the Product Owner to keep all stakeholders informed and align them with the goals of the product.
To refine the backlog and map user stories, visual tools like Miro and Lucid Chart are useful for creating interactive diagrams and workflows. These tools allow Product Owners to visually organize user stories and features, which can facilitate communication with stakeholders and sprint planning.
Finally, resources like Scrum.org and Agile Alliance offer training materials, templates, and best practices to help Product Owners continuously improve their skills and stay up to date with the latest trends in Agile and Scrum methodologies. By using these tools and resources, Product Owners can effectively manage the product backlog, prioritize features, and ensure that their team is always providing value.
In addition to the tools mentioned, Product Owners can also benefit from tools like Product Plan and Aha! that are designed for road mapping and product strategy. These tools allow Product Owners to define long-term product goals, visualize key milestones, and align the product roadmap with stakeholder expectations and business goals. They provide clear strategic insights that help communicate product direction, ensuring that the entire team understands the larger vision beyond immediate sprint goals.
User feedback tools like SurveyMonkey or Type Form can also play an important role in collecting customer information that informs product decisions. These tools allow Product Owners to gather and analyze feedback directly from users, which helps prioritize the most valuable features in the product backlog. Incorporating this feedback into the refinement of the order book ensures that the product is always evolving according to customer needs and market demands.
Another useful resource is Google Analytics or other analytics platforms, which provide real-time data on how users interact with the product. This data-based approach allows Product Owners to track user behavior, identify pain points, and measure the impact of new features. By understanding user statistics and analytics, Product Owners can make informed decisions about feature prioritization and product enhancements.
Finally, community platforms such as Slack groups or Agile forums allow Product Owners to engage with other Agile practitioners. These platforms provide a space to ask questions, share experiences, and learn from the successes and challenges of others in applying Scrum methodologies. Being part of an active Agile community helps Product Owners stay up to date with industry best practices and trends, ensuring continuous improvement and growth in their role.
PREPARATION FOR Scrum CERTIFICATION
Overview of Scrum certifications
Scrum certifications are designed to validate an individual's knowledge and expertise in Scrum methodology, making them valuable assets for professionals who want to advance their careers in Agile project management. The certifications are offered by a variety of recognized organizations, with the most popular being Scrum.org, Scrum Alliance, and Scaled Agile. These certifications cover various roles within Scrum, including Scrum Masters, Product Owners, and development team members.
- ScrumMaster Certified (CSM): Offered by the Scrum Alliance, this certification is ideal for people who want to become Scrum Masters. This requires training and passing an exam. The CSM focuses on the core principles of Scrum, the Scrum framework, and the role of the Scrum Master.
- Professional Scrum Master (PSM): Provided by Scrum.org, PSM is one of the most respected Scrum certifications. It comes in several levels (PSM I, II, III) and does not require any formal training before taking the exam. The PSM assesses an individual's practical Scrum knowledge and ability to apply Scrum principles in real world scenarios.
- Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO): Also from the Scrum Alliance, the CSPO is designed for people who aspire to become a Product Owner. This certification focuses on backlog management, stakeholder collaboration, and maximizing the value provided by the Scrum team.
- Professional Scrum Product Owner (PSPO): Another Scrum.org certification, PSPO validates an individual's ability to manage the product backlog and maximize product value. Like the PSM, it comes in several levels and tests the candidate's thorough understanding of product ownership.
- Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) certifications: For people working in large organizations who use the Agile method at scale, SAFe certifications offer training on implementing and managing Agile at the enterprise level. The most popular certifications include SAFe Agilist and SAFe Scrum Master.
Exam content
The content of Scrum certification exams varies by certification body and level, but they generally cover key aspects of the Scrum framework, roles, events, and artifacts.
- Scrum Framework: Most exams start by assessing your knowledge of fundamental Scrum concepts, including roles (Scrum Master, Product Owner, Development Team), events (sprint planning, daily meetings, sprint reviews, and retrospectives), and artifacts (product backlog, sprint backlog, increment). You need to understand how these elements work together and how Scrum facilitates continuous delivery and improvement.
- Roles and responsibilities in Scrum: Exams will generally test your understanding of each role in Scrum. For example, a Scrum Master certification exam will focus primarily on the responsibilities of the Scrum Master, how they organize Scrum events, and how they remove obstacles. Likewise, a Product Owner Exam will test your ability to manage the backlog, prioritize tasks, and maximize product value.
- Agile principles and values: Scrum is based on the Agile Manifesto, so exam content often includes questions about Agile values and principles. You will need to demonstrate your understanding of how the Agile philosophy guides Scrum practices, with an emphasis on collaboration, flexibility, and customer satisfaction.
- Sprint planning and execution: Many exam questions will discuss how sprints are planned and executed. You need to know how to estimate tasks, allocate work, manage priorities, and ensure sprint goals are met. This often includes scenarios where you need to apply your knowledge to solve problems or optimize processes during a sprint.
- Facilitation and problem solving: During Scrum Master exams, you will often face questions about how to facilitate Scrum events and resolve team conflicts. You may need to understand how to train the team, remove obstacles, and ensure that the team follows Scrum practices.
- Metrics and continuous improvement: For most exams, it's critical to understand Scrum metrics such as velocity, summary charts, and how to use these tools to drive continuous improvement. You will need to demonstrate your ability to use metrics to monitor progress and improve team performance in subsequent sprints.
- Scaling Scrum: For more advanced certifications, you may encounter questions about how Scrum can be extended to multiple teams, for example through the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), Scrum of Scrums, or LeSS (Scrum at Scale). These questions test your knowledge of managing larger projects or enterprise level Scrum implementations.
By preparing for these exam topics, candidates can gain a solid understanding of Scrum and Agile practices, which will enable them to successfully complete their Scrum certification journey.
Effective study strategies
Preparing for a Scrum certification requires a structured and focused approach to ensure success. One of the most effective study strategies is to start with a thorough review of the Scrum Guide, which describes Scrum's core principles, roles, and processes. This guide is the core resource for most Scrum certifications, so being familiar with it is essential. Reading and reviewing the Scrum Guide will help you deepen your understanding of key concepts.
Next, create a study plan that divides topics into manageable sections, allocating specific time to each area of exam content, such as Scrum roles, events, and artifacts. Studying in short, focused sessions with regular breaks can improve retention. Using active memorization, a technique that allows you to test yourself on key concepts without looking at the material, can help strengthen your understanding and identify gaps in your knowledge.
It is also important to use multiple study resources. In addition to the Scrum Guide, consider enrolling in online courses or participating in workshops that offer practical information on how Scrum is implemented in real world environments. Some platforms, such as Scrum.org or Scrum Alliance, offer practice exams and quizzes that replicate the style of questions you'll encounter during the certification test.
Group study sessions with other Scrum certification candidates can also be beneficial. These sessions allow you to discuss concepts, clarify doubts, and gain new perspectives on Scrum practices. Additionally, using visual aids such as diagrams and flowcharts can help you better understand complex processes such as sprint planning, backlog refinement, and Scrum event flow.
Practices and simulations
Simulations and practical applications are a great way to consolidate your Scrum knowledge and prepare for the exam. Many Scrum certifications, especially for Scrum Masters and Product Owners, require understanding how to apply Scrum practices in real world scenarios. Participating in Scrum simulations, whether as part of a course or as a team, allows you to experience Scrum events firsthand, such as sprint planning, daily meetings, and retrospectives.
A common simulation technique is role-playing in which participants take on various Scrum roles (Scrum Master, Product Owner, or Development Team Member) and follow a simulated sprint. It's a practical opportunity to practice problem solving, prioritizing tasks, and facilitating team collaboration, allowing you to better understand roles and responsibilities within Scrum.
Mock exams are another essential tool in preparing for Scrum certification. Taking timed practice tests will help you become familiar with the exam format and identify areas that require additional review. You will also be more comfortable managing your time during the exam itself. Many platforms offer mock exams designed specifically for certifications like CSM or PSM, providing questions that look a lot like the real test.
Finally, applying Scrum in practice in your current work environment is one of the best ways to prepare. If possible, try to implement Scrum practices within your team or take on Scrum responsibilities. By learning firsthand about the challenges and nuances of Scrum, you'll have a more intuitive understanding of the framework, making it much easier to understand and apply exam content.
Additional resources
As you prepare for Scrum certification, using a variety of resources can improve your understanding and your chances of success. Here are some recommended resources to complete your study:
The Scrum Guide: Written by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland, this is the ultimate Scrum guide. It describes the framework, roles, events, and artifacts that form the foundation of Scrum. The guide is available free online and should be your primary study resource for any Scrum certification.
Scrum.org: Scrum.org offers detailed information on Professional Scrum certifications, including PSM and PSPO. It offers practice assessments, open assessments, and learning paths tailored to different roles. The website also has interesting articles, case studies, and webinars on Scrum topics.
Scrum Alliance: This organization offers various certification programs, including CSM and CSPO. They provide a wide range of resources including Scrum user groups, webinars, and workshops. Scrum Alliance also has a community where you can connect with other Scrum professionals to share tips and advice.
Books: Some key books can deepen your knowledge:
- “Scrum: The Art of Doing Twice the Work in Half the Time” by Jeff Sutherland: This book provides practical information on how Scrum can be applied in a variety of contexts.
- “Scrum Mastery: From Good to Great Servant-Leadership” by Geoff Watts: a valuable resource for those who want to excel in the Scrum Master role, this book focuses on leadership and facilitation skills.
- “The Professional Product Owner” by Don McGreal and Ralph Jocham: Ideal for Product Owners, this book discusses essential strategies for maximizing product value.
Using these resources will provide a comprehensive foundation for understanding Scrum, allowing you to effectively prepare for your certification and apply your knowledge in concrete scenarios.