In today's data-driven world, the ability to effectively analyze and visualize data is more critical than ever. Businesses, governments, and organizations around the world rely on data to make informed decisions, uncover insights, and drive innovation. However, the vast amount of data available poses a unique challenge: how do you turn raw data into actionable information?
Power BI has quickly become a leading business intelligence tool, known for its user-friendly interface and robust features that make Data Analysis accessible to users of all skill levels. Python, on the other hand, is renowned for its flexibility and power in managing complex data manipulations and advanced analytics.
Whether you're a business analyst looking to improve your reporting skills, a data scientist looking to integrate advanced Python visualizations into your Power BI dashboards, or a developer looking to automate and scale your data flows, this guide has something for you.
Over the chapters, you'll learn how to take advantage of the intuitive features of Power BI to create dynamic and interactive reports, as well as how to harness the power of Python to create personalized, advanced visualizations that go beyond the standard offerings of most business intelligence tools. You'll explore concrete use cases, practical examples, and best practices that allow you to extract deeper insights from your data and communicate it effectively to your audience.
This digital guide is more than just a technical manual; it's a guide to transforming the way you think and interact with data. By combining the strengths of Power BI and Python, you'll be able to create visualizations that not only tell a story but also generate actionable results.
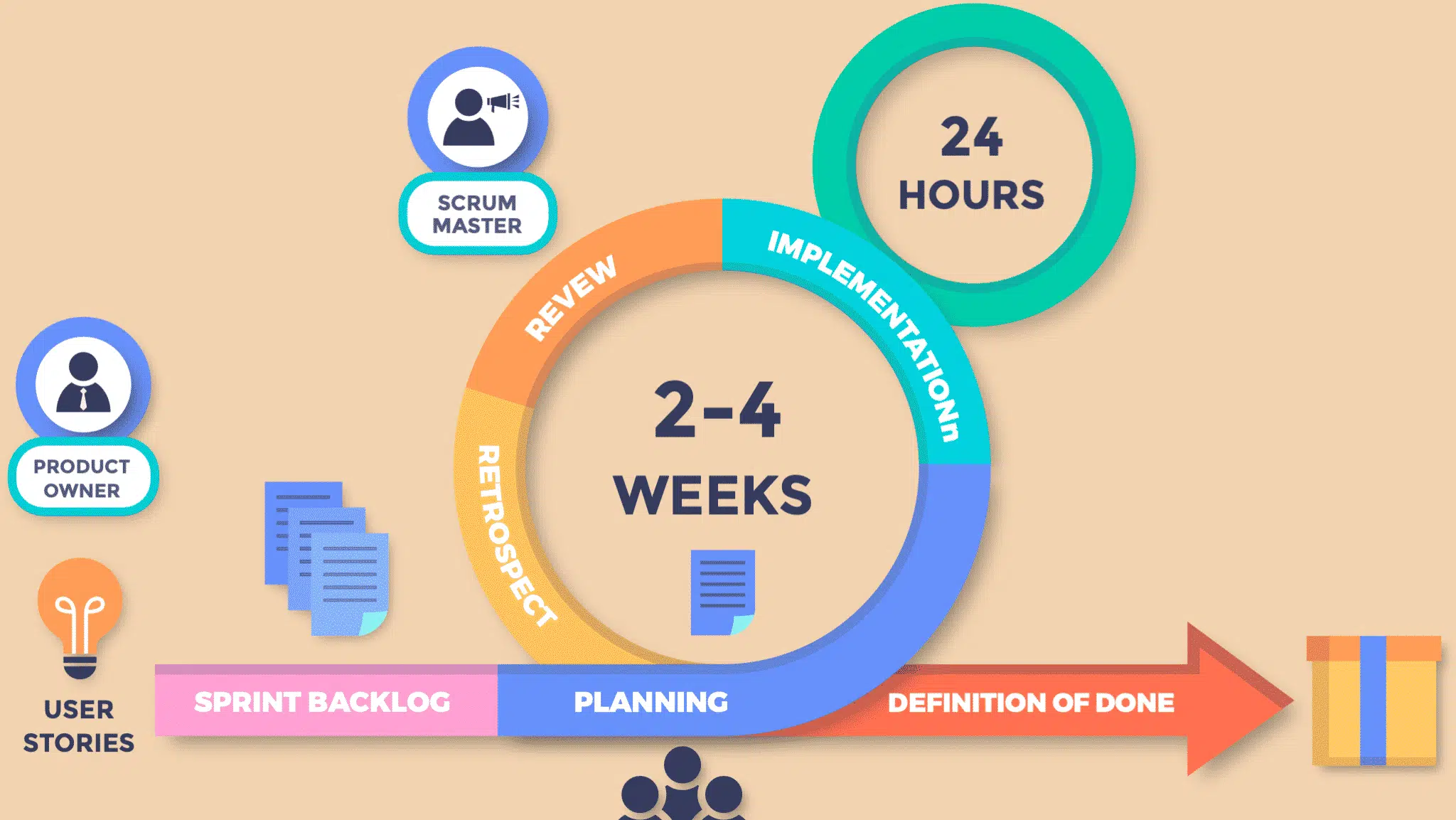
POWER BI OVERVIEW
Power BI is a powerful business analytics tool developed by Microsoft, designed to help organizations transform raw data into relevant information. It allows users to connect to different data sources, visualize data through interactive reports and dashboards, and share that information across their organization. With its user-friendly interface, robust data integration features, and dynamic visualization tools, Power BI has become an essential platform for businesses that want to make data-driven decisions. This section explores the main features of Power BI, from its core components to practical applications across industries, providing a comprehensive overview for new and experienced users alike.
What is Power BI?
Power BI is a suite of business intelligence (BI) tools developed by Microsoft that allows users to analyze and visualize data from a variety of sources. It is designed to provide interactive information through intuitive reports, dashboards, and data models. Power BI offers a range of components, including Power BI Desktop, Power BI Service, and Power BI Mobile, each addressing different aspects of Data Analysis and sharing. Whether you're dealing with complex data sets or simple data queries, Power BI's versatile platform allows you to connect, transform, and visualize data seamlessly.
Benefits of using Power BI for Data Analysis
Power BI is designed with accessibility in mind, making it easy for users of all skill levels to create and share reports without extensive training. Power BI supports a wide range of data sources, from Excel spreadsheets and SQL databases to cloud services like Azure, allowing comprehensive analysis of data from multiple origins.
Power BI's rich library of visuals, including tables, charts, and maps, allows users to create dynamic, interactive reports that make complex data easier to understand. Power BI provides real-time access to data, allowing users to make informed decisions based on the most up-to-date information.
Power BI makes collaboration easy through its cloud service, allowing teams to share reports and dashboards securely and work together on Data Analysis projects.
The core principles of Power BI
User interface and navigation:
The Power BI user interface is designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, allowing users to quickly access its powerful features. When you open Power BI Desktop, you're greeted by a clean workspace with a ribbon at the top, just like other Microsoft Office products. The ribbon provides quick access to essential tools and options, such as importing data, creating visuals, and managing queries.
On the left side, you'll find three main views:
- Report view: The default view in which you design and edit reports. You can drag and drop data fields onto the canvas to create visuals, customize them, and organize them into dashboards.
- Data View: This view allows you to examine and manipulate the underlying data that you imported into Power BI. Here you can view tables, apply filters, and perform data transformations.
- Model view: In this view, you can manage relationships between different data tables, allowing you to create a robust data model that underlies your reports.
The right side of the interface contains the Fields panel, where you can access all of the data fields available in your dataset, and the Visualizations panel, where you can choose from a variety of visual elements such as tables, charts, and maps.
Overview of the main components:
Power BI desktop:
Power BI Desktop is the primary tool for creating reports and data models. This is where most users start their transition to Power BI.
It offers a comprehensive set of tools for connecting, transforming, modeling, and visualizing data. Power BI Desktop allows you to create complex reports with multiple pages, use DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) for advanced calculations, and set up relationships between data.
Once reports are created, they can be published to the Power BI service for sharing and collaboration.
Power BI service:
The Power BI service, also known as Power BI Online or Cloud Service, is a cloud-based platform that allows users to share, collaborate, and interact with reports and dashboards.
It allows for real-time data updates, report distribution, and collaboration between teams. Users can create and manage workspaces, set up data refresh schedules, and access shared content through web browsers.
Power BI Service is ideal for sharing reports with a wider audience, managing user permissions, and integrating Power BI content into other Microsoft services like Teams and SharePoint.
Power BI Mobile:
Power BI Mobile is a mobile application that allows users to access and interact with Power BI reports and dashboards from anywhere.
The app is available for iOS, Android, and Windows devices and offers features like touch navigation, offline access, and push notifications for data alerts.
Power BI Mobile is ideal for leaders and team members who need to stay connected to their data, whether on the go or away from the office.
Together, these components provide a comprehensive platform for analyzing, visualizing, and sharing data, allowing users to harness the full power of their data regardless of location or device.
Data connection and integration
Compatible data source types:
Power BI is known for its versatility in connecting to a wide range of data sources. Whether your data is stored on-premises or in the cloud, Power BI can integrate with multiple platforms, making it easy to bring all of your data together in one place. Some of the most common data sources that are compatible with Power BI include:
- Excel and CSV files: Easily import spreadsheets and flat files, which are often used for small data sets and ad hoc analyses.
- SQL databases: connect directly to SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and other relational databases to access structured data.
- Cloud-based services: Integrate cloud services like Azure SQL Database, Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, and others for large-scale data processing.
- Online services: extract data from popular online services like Google Analytics, Salesforce, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
- SharePoint and OneDrive: Connect to OneDrive SharePoint lists, libraries, and files for seamless access to documents and collaboration tools.
Simple procedures for importing and connecting to data:
Power BI simplifies the process of importing and connecting to data, even for users with limited technical expertise. Here's a simple, step-by-step guide to get you started:
Start by launching Power BI Desktop, where you'll create your reports.
On the Home tab, click the “Get Data” button. A pull-down menu is displayed, listing the current data sources. If your source is not listed, click “More” to see the full list of supported data connections.
Select the type of data source you want to connect to (for example, Excel, SQL Server, Web). A dialog box appears asking you to enter the required login information, such as file paths, server names, or URLs.
After entering login details, click “Connect.” Power BI will attempt to establish a connection with the data source. If successful, an overview of the data will be displayed.
You can choose specific tables or sheets to import, and even filter or transform data before loading it into Power BI.
If your data needs to be cleaned or transformed, click “Transform Data” to open the Power Query editor. Here you can perform tasks such as removing duplicates, dividing columns, changing data types, etc.
Once you are happy with the transformations, click “Close and load” to import the data into Power BI. Once the data is loaded, you can now start creating visuals, creating reports, and exploring the information you've gathered.
Power BI's ability to connect to a wide range of data sources, coupled with its user-friendly import process, ensures that users can quickly and effectively integrate their data into the platform for analysis and reporting purposes. Whether you're working with simple spreadsheets or complex cloud-based databases, Power BI provides the tools you need to integrate your data seamlessly.
Creating reports and dashboards
Basic principles for designing interactive reports:
Creating effective, interactive reports in Power BI isn't enough to simply place visuals on a canvas. Here are some fundamental principles that will guide you:
Understand the needs and expectations of the target audience for your report. Adapt content, visuals, and level of detail to suit their needs, ensuring that the report effectively communicates the information that is needed.
Opt for the clarity and simplicity of your design. Avoid cluttering the report with too many visuals or excessive information. Focus on key metrics and information that directly address the needs of your audience.
The consistency of the layout makes it easier for users to navigate and understand the report. Align visuals perfectly, use consistent colors and fonts, and maintain a logical flow from one visual to the next.
Power BI excels in terms of interactivity. Use slicers, filters, and explorations to allow users to explore data in greater detail. Interactive elements help users find answers to specific questions and deepen their participation in the report.
Use visual cues such as color codes, labels, and annotations to draw attention to the information that matters most. This allows users to quickly grasp key takeaways without getting lost in the details.
Before finalizing your report, test it with a small group of users to get their feedback. Adjust based on their feedback to improve the effectiveness of the report.
Use of standard visuals for dynamic dashboards:
Power BI offers a wide range of standard visuals that can be used to create dynamic and engaging dashboards. Here's how you can use some of the most common visuals effectively:
- Bar and column charts:
- Use case: ideal for comparing data across categories or over time.
- Tips: Use horizontal bar charts for category comparisons and vertical column charts for time series data. Combine them with exploration features to allow users to explore subcategories.
- Line and area charts:
- Use case: great for showing trends over time.
- Tips: Line charts are great for displaying continuous data, while area charts focus on the extent of change. Overlay multiple lines or areas to compare different measures or time periods.
- Pie and ring charts:
- Use case: useful for showing parts of a whole.
- Tips: Limit the number of slices to avoid clutter. Use these charts to show simple, high-level proportions and consider adding data labels for greater clarity.
- Maps:
- Use case: great for visualizing geographic data
- Tips: Use maps to highlight regional differences or trends. Power BI supports a variety of card types, including filled cards and bubble cards, each with different goals based on your data.
- Tables and matrices:
- Use case: essential for detailed presentation of data in tabular form.
- Tips: Use tables to show raw data with columns and rows. Matrix visuals allow for more complex hierarchical data, allowing users to pivot and delve into details.
- Maps and key performance indicators:
- Use case: ideal for highlighting key metrics and performance indicators
- Tips: Use graphics cards to show unique numbers or key performance indicators in a visible way. Combine them with conditional formatting to indicate whether the measures meet goals or require special attention.
- Trenchers:
- Use case: interactive tools to filter data on the dashboard.
- Tips: Use slicers to allow users to filter data by categories, dates, or other dimensions. Place them prominently on the dashboard for easy access.
- Scatter and bubble charts:
- Use case: useful for showing relationships between variables.
- Tips: Scatter charts are great for analyzing correlations, while bubble charts add a third dimension, with bubble sizes representing another variable.
To create a dynamic dashboard, combine these visual elements strategically:
Organize your visuals to tell a cohesive story. Start with high-level key performance indicators at the top of the page, followed by detailed visuals that provide more detailed information. Integrate slicers and filters that allow users to personalize their data view. Use bookmarks to create predefined views that users can switch between. If your data sources allow it, enable real-time data updates to keep the dashboard up to date and provide users with the most up-to-date information.
By following these principles and effectively using the standard visuals in Power BI, you can create reports and dashboards that are not only visually appealing but also highly functional and interactive, allowing users to explore data and discover insights with ease.
Data visualization
Selecting appropriate visualizations for different types of data:
Choosing the right visualization is critical to effectively communicate data information. The type of data you have will often dictate the most appropriate visualization. Here are some common data types and the visualizations that work best for them: Categorical
data:
- Bar charts: ideal for comparing data from different categories (for example, sales by region or by product type).
- Pie and ring charts: useful for showing the proportion of categories in a set (for example, market share by brand).
Time series data:
- Line charts: ideal for showing trends over time, such as monthly sales figures or temperature changes.
- Area charts: highlight cumulative changes over time, allowing you to show how values add up.
Numeric data:
- Histograms: effective for displaying the distribution of a single numerical variable (for example, income distribution).
- Scatter plots: perfect for identifying relationships between two numerical variables (for example, age in relation to income).
Geographic data:
- Maps (filled, bubble, or heat maps): essential for visualizing data that has a geographic component, such as population density or sales by location.
- Choropleth maps: color-coded maps that indicate the density or intensity of data in different regions.
Hierarchical data:
- Tree maps: useful for visualizing hierarchical data structures (for example, sales by product category and subcategory).
- Sunburst charts: Display hierarchical data in a radial layout, offering an alternative to tree maps.
Partial to integral relationships:
- Stacked bar charts: show how different pieces contribute to the overall picture in different categories (for example, sales by product type in regions).
- Waterfall charts: Show the cumulative effect of positive or negative values introduced sequentially.
Customizing visuals for a clear and concise presentation:
Customizing visuals in Power BI is critical to improving clarity and ensuring effective communication of your data story. Here are some key personalization techniques:
- Titles and labels:
- Clear titles: Always provide a descriptive title for each visual that clearly states what the visual represents. This allows users to quickly understand the context.
- Data labels: Use data labels to show the exact values on your charts. This is especially useful for bar, column, and pie charts where understanding accurate numbers is important.
- Color schemes:
- Consistent colors: Maintain a consistent color palette throughout your report to avoid confusion. Use colors strategically to highlight key data points or to differentiate categories.
- Conditional formatting: Apply conditional formatting to highlight data that meets certain criteria, such as sales goals or threshold limits.
- Axes and ladders:
- Axis labels: Ensure that the X and Y axes are clearly labeled with the units of measurement. This allows users to understand the scale and context of the data.
- Appropriate scaling: Adjust the axis scales to ensure that your data is presented proportionally. Avoid distorting the visual by using inappropriate scales.
Practical applications of Power BI
Power BI is a versatile tool that finds applications across a variety of industries, helping organizations leverage data for strategic decision-making, operational efficiency, and customer insights. Here are some practical Power BI use cases across industries:
1. Financial services:
- Use case: risk management and compliance reports
- Application: Financial institutions use Power BI to monitor and assess risks across portfolios, track regulatory compliance, and generate real-time reports for auditors and stakeholders. By integrating with various financial databases, Power BI allows users to visualize and analyze key risk indicators, ensuring rapid interventions.
2. Retail and E-commerce:
- Use case: sales performance and inventory management
- Application: Retailers use Power BI to track sales performance across stores, regions, and product lines. The tool allows inventory levels to be monitored in real time, helping businesses optimize inventory management and reduce overstock or out-of-stock situations. Power BI dashboards provide information on customer buying trends, allowing for targeted marketing and promotions.
3. Health care:
- Use case: patient care and operational efficiency
- Application: In the healthcare industry, Power BI is used to analyze patient data, track treatment outcomes, and manage hospital operations. Healthcare providers can visualize patient flow, monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as bed occupancy rates, and identify patient care trends, leading to improved service delivery and resource allocation.
DATA ANALYSIS WITH POWER BI
Introduction to Data Analysis
Basic concepts of Data Analysis:
Data analytics is the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data to discover useful information, draw conclusions, and facilitate decision-making. This involves a series of steps that help organizations make sense of their data, discover patterns, and identify relationships between variables. The basic concepts of Data Analysis are as follows:
- Data collection: collection of relevant data from a variety of sources, such as databases, surveys, or online platforms, to be analyzed.
- Data cleaning: preparing data by correcting errors, managing missing values, and removing duplicates to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Data transformation: converting raw data into a format suitable for analysis, which may involve normalizing data, aggregating values, or creating new calculated fields.
Importance of Data Analysis in decision making:
Data analysis plays a crucial role in modern decision-making processes across industries. Here are some of the main reasons why Data Analysis is essential:
Informed decision making: Data Analysis provides a factual basis for decisions, reducing the need for intuition or guesswork. By analyzing historical and real-time data, organizations can make choices that are informed and more likely to deliver positive results.
Identify trends and patterns: Through Data Analysis, businesses can identify trends and patterns that may not be immediately obvious. For example, analyzing sales data can reveal seasonal trends or patterns of consumer behavior, allowing businesses to adjust their strategies accordingly.
Improving efficiency: Data Analysis helps organizations identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. By analyzing operational data, businesses can streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve productivity.
Risk Management: Analyzing data related to financial transactions, market conditions, or customer behavior can help organizations assess risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. This proactive approach to risk management can prevent potential problems from getting worse.
Customer Information: Data Analysis allows businesses to better understand the preferences, needs, and behaviors of their customers. This information allows for more personalized marketing, better customer service, and the development of products or services that better meet customer demands.
Power BI tools and features for analytics
Use of filters and slicers to refine analyses:
Power BI provides powerful tools such as filters that allow users to refine their analyses and focus on specific subsets of data.
Filters:
Filter types: Power BI offers several types of filters, including visual-level filters (affecting only one visual), page-level filters (affecting all visuals on a report page), and report-level filters (affecting all visuals in the report).
Using filters: Filters can be applied by dragging and dropping fields into the filters panel. Users can then specify conditions (for example, greater than, equal) to show only relevant data. Filters are essential for refining large data sets to focus on specific segments, such as a particular time period, geographic region, or product category.
Slicers:
What are slicers? Slicers are visual tools that allow users to filter data interactively on the report page. They appear as buttons or pull-down lists on the report and can be used to filter visuals in real time by categories such as date, region, or product type.
Using Slicers: To add a slicer, drag a field into the report canvas and choose the “Slicer” visualization. Users can click on the slicer options to filter data instantly. Slicers are particularly useful for creating interactive reports where end users can easily explore different data views.
Overview of DAX functions:
DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) is a powerful Power BI formula language used to create custom calculations and aggregations.
What is DAX?
DAX looks like Excel formulas but is adapted to Power BI data models. It allows users to perform advanced calculations, create columns and calculated measures, and improve Data Analysis capabilities.
Common DAX functions:
SUM: add up the values in a column.
AVERAGE: Calculate the average of the values.
COUNTROWS: Count the number of rows in a table.
IF: create conditional logic.
CALCULATE: Modifies the context of a calculation, allowing for more complex aggregations.
Data preparation and transformation
Essential steps for cleaning and preparing data:
Prior to analysis, data often needs to be cleaned and transformed to ensure accuracy and relevance. The Power BI Power Query Editor provides a robust set of tools for this process.
- Data cleaning:
- Missing Data Management: Identify and correct missing data by filling in gaps, removing incomplete rows, or using statistical methods to estimate missing values.
- Eliminate duplicates: Ensure data integrity by removing duplicate records that may skew analysis results.
- Correct errors: Look for inconsistencies, such as incorrect data types, formatting issues, or typos, and correct them to maintain data quality.
- Data transformation:
- Data normalization: Standardize data in a consistent format, especially when combining data from multiple sources. This may involve converting text to upper and lower case, standardizing date formats, or unifying numerical scales.
- Data aggregation: Summarize data by grouping records together and calculating aggregate measures such as totals, averages, or numbers. This is especially useful for simplifying large data sets and focusing on high-level trends.
- Data merging: Combine data from different tables or sources using joins or merges, ensuring that the data is properly linked for analysis.
Data transformation with Power Query:
Power Query is a feature in Power BI Desktop that allows users to easily extract, transform, and load data (ETL). Here's how to use it for data transformation:
Access to the Power Query Editor:
In Power BI Desktop, click “Transform Data” to open the Power Query editor. This environment provides a comprehensive set of tools for data preparation.
Apply transformations:
- Delete columns: remove unnecessary columns that are not relevant to your analysis.
- Change data types: Ensure that each column contains the correct data type (for example, text, number, date).
- Split columns: Divide columns into multiple fields based on delimiters (for example, by dividing full names into first and last names).
- Pivot/Unpivot: Rotate the data to summarize it, or cancel the data to restructure it into a more analytically friendly format.
Analysis of trends and patterns
Methods for identifying trends and patterns:
Identifying trends and patterns in data is a key aspect of Data Analysis, allowing organizations to predict future outcomes and make informed decisions. Power BI offers several ways to discover this information:
- Time series analysis:
- Line charts: Use line charts to visualize data over time, making it easier to spot trends such as up or down movements. By plotting data points in chronological order, you can identify seasonal trends, cyclical trends, or long-term growth.
- Moving averages: Apply moving averages to mitigate short-term fluctuations and highlight long-term trends. This technique is useful for identifying the underlying trend in volatile data.
- Comparative analysis:
- Bar and column charts: compare data across categories or time periods to identify performance patterns. For example, comparing sales figures across regions or product lines can reveal which areas consistently perform well.
- Stacked charts: Use stacked bar charts or column charts to compare the contribution of different categories to a whole over time. This helps to understand changes in composition, such as changes in market share.
Use of analytical visuals to highlight results:
Power BI offers a range of analytics visuals that can be used to highlight trends and patterns in your data:
- Line and area charts:
- Highlight trends: Line charts are great for showing trends over time, with the ability to add markers or data labels to highlight key points or changes.
- Area charts: Use area charts to highlight the magnitude of trends by shading the area below the line, which can make cumulative trends more apparent.
- Clustered and stacked bar charts:
- Focus on comparisons: Clustered bar charts allow you to compare multiple series side by side, making it easy to visualize relative performance across categories. Stacked bar charts, on the other hand, show the cumulative effect of the various categories, highlighting their contribution to the total.
- Waterfall charts:
- Visualizing changes: Waterfall charts are ideal for visualizing the cumulative effect of sequential data points, such as revenue components or budget changes. Each bar on a waterfall chart represents a stage of accumulation, making it easy to see how the various items contribute to the overall total.
Presentation of results and reports
Structuring and formatting reports for effective communication:
Presenting data effectively in Power BI requires careful structuring and formatting to ensure that information is communicated clearly and convincingly. Here are some best practices: Clear and logical
structure:
Start with an overview or summary that highlights key findings or ideas. This helps to define the context of the report.
Organize the report into sections that flow together logically, for example by topic, time, or department. Each section should contain relevant visuals and comments that explain the results.
Consistent formatting:
Use consistent themes and color combinations throughout the report to maintain a professional appearance. Consistent use of colors can also help reinforce key points, such as using green for positive trends and red for negative trends.
Choose a legible font and maintain consistent font sizes and styles for titles, subtitles, and body text. Align visuals and text boxes perfectly to create a clear and organized layout.
Focus on key information:
Use bold text, different colors, or legends to highlight key information or data points. This draws the reader's attention to the most important parts of the report.
Add annotations or comments directly onto visuals to explain important data points, trends, or outliers. This ensures that the audience understands the context and implications of the data.
Sharing and collaborating on Power BI reports:
Power BI offers a variety of ways to share reports and collaborate on reports to ensure that information reaches the right people in an organization:
Publishing to Power BI Service:
After creating a report in Power BI Desktop, you can publish it to the Power BI service. This cloud-based platform allows you to share reports with colleagues, who can view and interact with the report using a web browser.
Use Power BI service workspaces to organize and manage shared reports and dashboards. Workspaces also allow for collaboration between team members, who can co-write reports, provide feedback, and review changes.
DATA VISUALIZATION WITH PYTHON AND POWER BI
Introduction to data visualization
Importance and impact of data visualization:
Data visualization is the graphical representation of data and information. Using visual elements such as tables, graphs, and maps, data visualization tools provide an accessible way to see and understand data trends, outliers, and patterns. The importance and impact of data visualization in today's data-driven world cannot be overstated: Data
visualization makes it possible to simplify complex data by presenting it in a visual context. This allows users to quickly grasp complex concepts, identify trends, and make connections between variables that may not be immediately obvious in the raw data.
Visualized data provides information that enables faster, more informed decisions to be made. When data is presented visually, decision makers can more easily identify problems, opportunities, and trends, leading to more strategic and effective actions.
Comparison of the visualization features of Power BI and Python:
While Power BI and Python are powerful data visualization tools, they have slightly different goals and distinct benefits:
Power BI:
Power BI is designed for business users, with a user-friendly interface that makes it easy to create interactive reports and dashboards without requiring extensive technical skills. Users can drag and drop data fields to create visuals and customize them with just a few clicks.
Power BI comes with a wide range of predefined visuals, including bar charts, line charts, maps, etc. It also supports custom visuals from the Power BI marketplace, allowing users to extend its functionality.
Python:
Python, with libraries like Matplotlib, Seaborn, and Plotly, offers immense flexibility in creating custom, complex visualizations. Users can create everything from basic graphics to sophisticated multi-level visuals tailored to specific needs.
Python's visualization capabilities are tightly integrated with its Data Analysis and machine learning libraries, such as Pandas, NumPy, and Scikit-learn. This allows for smooth transitions from data manipulation to visualization, often in a single script.
Summary of the comparison:
| Functional/Appearance | Power BI | Python |
| Ease of use | User friendly interface, drag-and-drop functionality, minimal coding required | Requires coding, more suitable for users with programming knowledge |
| Personalization | Limited to embedded visuals and custom visuals from the marketplace | Highly customizable, can create unique and complex visuals using libraries like Matplotlib and Seaborn |
| Interactivity | High interactivity with slicers, filters, and exploration tools; ideal for dashboards | Interactivity is possible with additional libraries (for example, Plotly) but generally requires more configuration |
| Integration | Integrates perfectly into the Microsoft ecosystem (Excel, Azure, SharePoint) | Integrates with various Data Science and machine learning libraries; more flexible but requires configuration |
| Data processing | Integrated tools for data transformation and modeling that are easy to use | Advanced data processing capabilities including complex transformations, automation, and machine learning |
| Real-time data | Supports real-time data updates and live connections to data sources | Real-time data management possible but requires custom implementation |
| Best suited for | Business analysts, report developers, and users who need fast, interactive dashboards | Data scientists, developers, and analysts who need deep customization, advanced analytics, and automation |
| Learning curve | Relatively low; suitable for beginners and intermediate users | Steeper learning curve; requires an understanding of programming concepts |
Overview of visualization tools and libraries
Overview of the most popular Python libraries: Matplotlib and Seaborn
Python offers a rich ecosystem of libraries for visualizing data, each designed to meet different needs. Two of the most popular libraries are Matplotlib and Seaborn, both of which are powerful tools for creating a wide range of visualizations.
Matplotlib:
Matplotlib is one of the oldest and most used Python libraries for creating static, interactive, and animated visualizations. It provides a comprehensive suite of tools for generating charts, graphs, and other graphical representations of data.
Matplotlib is very versatile and allows users to create a variety of visualizations including line charts, scatter charts, bar charts, histograms, etc. It also provides precise control over every aspect of a graph, from colors and line styles to axis labels and figure sizes.
Matplotlib's numerous customization options make it ideal for producing publication-quality visuals. Users can create complex layouts with multiple paths, annotate graphics, and even draw shapes and text directly onto figures.
Although Matplotlib is primarily designed for static visualizations, it can be integrated with other libraries like Plotly or used in interactive environments like Jupyter Notebooks to add interactivity.
Seaborn:
Seaborn is built on Matplotlib and provides a high-level interface for creating more engaging and informative statistical graphs. It simplifies the process of generating complex visualizations and is particularly suitable for Data Analysis tasks.
Seaborn is designed for visualizing statistical data and excels at creating heatmaps, categorical diagrams (such as box charts and fiddle charts), and multi-faceted graphs that present multiple variables in a single figure. It also comes with built-in themes and color palettes to improve the aesthetics of the paths.
One of Seaborn's biggest strengths is its ease of use. With just a few lines of code, users can create complex plots that would require a lot more effort with Matplotlib alone. Seaborn handles much of the underlying work, such as configuring the axes, managing the aesthetics of the paths, and managing the data blocks directly.
Seaborn integrates seamlessly with Pandas, allowing users to directly visualize data stored in Pandas DataFrames. This makes it a great choice for exploratory Data Analysis, where quick and easy data visualization is essential.
Benefits of knowing Python to improve Power BI visualizations
While Power BI is a powerful data visualization tool, integrating Python into your workflow can dramatically improve your ability to create advanced, customized visualizations. Here are some of the benefits of knowing Python when working with Power BI:
- Advanced customization:
- Complex visuals: Python allows you to create complex, highly customized visualizations that may not be possible with Power BI's built-in visuals. For example, if you need a specific chart type that Power BI doesn't support natively, you can create it in Python using libraries like Matplotlib or Seaborn and then integrate it into your Power BI report.
- Unique visuals: Python provides the flexibility to design unique visuals tailored to your specific needs, such as custom scatterplots with annotations, heatmaps with specialized color scales, or interactive charts using libraries like Plotly.
- Seamless integration:
- Python scripts in Power BI: Power BI allows users to run Python scripts directly on the platform. That means you can use Python to process and visualize data and then integrate the results into your Power BI dashboards. This integration opens up a new world of possibilities by combining the interactivity of Power BI with the advanced visualization features of Python.
- Data manipulation and analysis: Python is not only for visualization, it is also a powerful tool for data manipulation and analysis. By taking advantage of Python in Power BI, you can perform complex data transformations, statistical analyses, and machine learning tasks before visualizing the results in your reports.
Techniques for creating effective visualizations
Creating effective visualizations is key to clearly conveying data information and making a lasting impact on your audience. Here are some best practices to ensure that your visualizations are both clear and compelling:
Understand your audience:
Adapt your visualizations to the level of knowledge and needs of your audience. For example, executives may need high-level summaries, while analysts may need detailed, data-rich visuals. Identify the most important data points or trends that your audience needs to understand and highlight them in your visuals.
Choose the appropriate visualization type:
Use the type of visualization that's appropriate for the data you're presenting. For example, use line charts to show trends over time, bar charts to compare categories, and scatter charts to show relationships between variables. Choose the simplest visualization that effectively communicates your message. Avoid overly complex visuals that can cause confusion instead of clarifying.