In the fast-paced world of technology, Full Stack development has become one of the most dynamic and sought-after skills in the software industry. The ability to design, develop, and manage both the frontend and the backend of web applications gives Full Stack developers a unique advantage, allowing them to successfully complete a project from start to deployment.
Becoming a Full Stack developer is both challenging and rewarding. This requires mastering a broad range of technologies, from user interface design to front-end frameworks, to server-side logic, databases, and deployment strategies. With the rapid pace of innovation, the tools and techniques used in Full Stack development are constantly evolving.
Throughout this guide, we'll explore the full spectrum of Full Stack development, starting with the fundamental concepts of front-end technologies such as HTML, CSS, and Javascript. Next, we'll discuss modern front-end frameworks like React and Vue.js, which have revolutionized the way we create interactive and responsive user interfaces. On the backend, we'll cover the basics of server-side programming with Node.js, Python, and PHP, and explore the intricacies of working with databases, both relational and NoSQL.
Access a future-proof career in tech with our programs and courses with payment plans spread over 6 months starting at €375/month. Join us now!
But this guide goes beyond simple coding. We'll also discuss best practices in web security, DevOps, and deployment to ensure that your applications are not only functional, but also secure, scalable, and maintainable. Real-world examples and case studies will provide practical information that will help you understand how these technologies combine to create robust and comprehensive web applications.
Whether you are a developer looking to broaden your skills or a beginner starting out in the world of web development, this guide is structured to provide you with a solid foundation and guide you through more advanced topics. You'll have the tools and knowledge to confidently take on comprehensive development projects, turning ideas into reality through a comprehensive understanding of frontend and backend.
Introduction
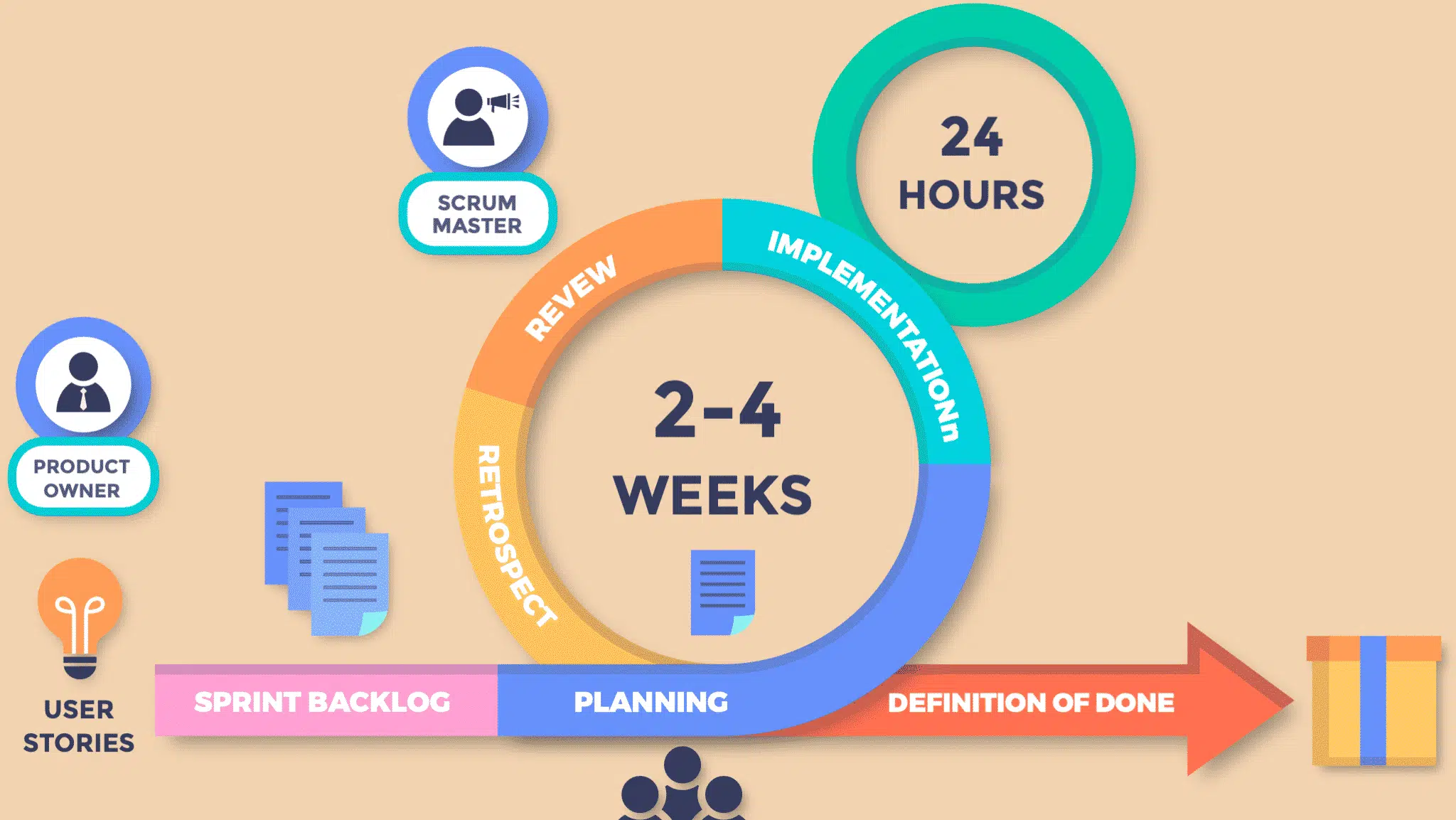
In today's digital landscape, Full Stack development has become a crucial skill for web developers, allowing them to work on both the front-end and the back-end of web applications. A Full Stack developer has the knowledge and expertise to manage all aspects of a web project, from user interface design to database and server management. This section will introduce you to the fundamentals of Full Stack development, including an overview of key technologies, the roles and responsibilities of a Full Stack developer, and the benefits of mastering both ends of the development spectrum. Whether you are an aspiring developer or an experienced programmer looking to broaden your skills, this introduction will lay the foundation for your journey into the world of Full Stack web development.
What is Full Stack Development?
Full Stack development refers to the practice of working on both the Front End (client side) and Back End (server side) parts of a web application. A Full Stack developer masters both aspects, allowing them to create web applications that are fully functional from start to finish. On the front-end, developers use technologies like HTML, CSS, and Javascript to design the visual elements and user interfaces that users interact with. On the Back End, they use programming languages such as Python, Java, or Node.js, as well as databases such as MySQL, MongoDB, or PostgreSQL, to manage the server, application logic, and database interactions.
Why Full Stack Development is a Key Skill for the Future:
In an increasingly digital world, the demand for multi-skilled developers who can handle all aspects of web development is growing rapidly. Full Stack developers are in high demand because they can manage projects more effectively, bridging the gap between different parts of a development team. They provide a comprehensive understanding of how web applications work, resulting in more consistent and comprehensive products. As technology continues to evolve and the boundaries between front-end development and core development blur, mastering Full Stack development ensures developers have the skills they need to adapt to new challenges and opportunities in the tech industry.
Why choose Full Stack Development?
Career opportunities: Full Stack
development offers a wide range of career opportunities across a variety of sectors. As a Full Stack developer, you're not limited to working in a single area of web development; rather, you have the skills to contribute to front-end and back-end projects. This versatility makes Full Stack developers highly sought after by employers, resulting in increased job opportunities and competitive salaries. Whether you're looking to work for a tech giant, a Startup, or as a freelancer, mastering Full Stack development opens doors to numerous career paths.
Job flexibility:
One of the main benefits of being a Full Stack developer is the flexibility it offers. With expertise in front-end and back-end development, you can work on various types of projects, whether it's building a complete web application from scratch or contributing to specific parts of an existing project. This flexibility allows Full Stack developers to move between roles and responsibilities within a team, making them invaluable assets in dynamic work environments.
Benefits for career transition or complementing another professional activity: Full
development is a great choice for those who want to make the transition to a technological career or complete another professional activity. For people from a different industry, comprehensive development learning provides a comprehensive set of skills that allows for a smoother transition to web development. The ability to understand and work on both sides of web applications can be especially beneficial for those with experience in related fields, such as graphic design, project management, or marketing, as it allows them to bridge the gap between their previous expertise and their new technical role.
Access a future-proof career in tech with our programs and courses with payment plans spread over 6 months starting at €375/month. Join us now!
Web Development Basics
To fully understand Full Stack development, it is important to first understand the fundamental components of web development: the front-end, the back-end, and the databases. These three areas are the core of any web application and mastering them is essential to become a competent Full Stack developer.
Front End
The front-end, also called client-side, is the part of a web application that users interact with directly. It includes everything users see and experience, from layout and design to the buttons, forms, and text that they interact with. The main technologies used in front-end development are HTML (HyperText Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), and Javascript. HTML provides the structure of a web page, CSS handles style and visual design, and Javascript adds interactivity and dynamic behavior.
Back End
The Back End, or server side, is the engine that powers the web application in the background. It manages the logic, database interactions, authentication, and data processing that make the front-end experience possible. Back-end development involves working with server-side programming languages such as Python, Java, Ruby, or Node.js. This also includes managing servers, processing API (application programming interface) requests, and ensuring the fluidity of data between the server and the client.
Frameworks Front End
Introduction to front-end frameworks
Front-end frameworks have become the lifeblood of modern web development, streamlining the process of building responsive, dynamic, and user-friendly web applications. These frameworks provide standardized, pre-written code that simplifies common tasks, such as layout design, user interface components, and state management, allowing developers to focus on the unique aspects of their projects rather than reinventing the wheel for each new application.
One of the main reasons front-end frameworks are critical is their ability to promote consistency and efficiency within development teams. By offering a set of predefined rules and components, frameworks allow developers to maintain a consistent appearance across the application, even when multiple people are working on different parts of the project. This consistency not only improves the user experience, but also speeds up the development process by reducing time spent on repetitive tasks.
Comparison of the main front-end frameworks
In the world of front-end development, three main frameworks dominate the landscape: Vue.js, React, and Angular. Each of these frameworks has its own strengths and is adapted to different types of projects and developer preferences. Here's a comparison of their top features and benefits, especially from a newbie perspective.
1. Vue.js
Characteristics:
- Progressive framework: Vue.js is designed to be adopted gradually, which means you can start using it for a small portion of your project and expand it gradually.
- Two-way data binding: Like Angular, Vue.js allows for two-way data binding, making it easy to sync data between the model and the view.
Benefits for newbies:
- Soft learning curve: Vue.js is known for its simplicity and ease of use, making it a great choice for beginners who want to get up to speed quickly with front-end development.
- Clear documentation: Vue.js offers comprehensive and accessible documentation, which is extremely useful for beginners.
2. React
React focuses on creating user interfaces using reusable components, which promotes code reusability and maintainability. React uses a virtual DOM to effectively update and display components, resulting in high performance even with complex applications. React's unidirectional data link ensures that data flows in one direction only, making code more predictable and easier to debug.
Benefits for newbies:
- Strong ecosystem: React has a vast ecosystem of libraries and tools, which means newbies have access to a wide range of resources and third-party integrations.
- Community support: React, one of the most popular frameworks, has an active community and a multitude of tutorials, guides, and examples available online.
3. Angular
Angular is a comprehensive solution for front-end development, offering everything from routing to state management, ready to use. Angular's two-way data linking automatically synchronizes data between the model and the view, simplifying the development process.
Using frameworks in web development
To better understand how front-end frameworks like Vue.js, React, and Angular can be integrated into real-world projects, let's look at a few case studies that highlight how they can be applied in different scenarios.
1. Vue.js on a small business website:
Project Overview:
A local bakery wanted to reorganize their website to include an online ordering system, a blog, and a gallery showcasing their products. The project required a lightweight and easy to maintain solution that could keep up with the evolution of the business.
Framework selection:
Vue.js was chosen for this project because of its simplicity and ease of integration into existing code. The progressive nature of Vue.js allowed developers to gradually introduce it to the existing website without a complete redesign.
Integration and result:
The development team used Vue.js to create a dynamic interface for the online ordering system, allowing users to browse products, add items to their cart, and make purchases using a smooth and interactive interface.
Additional tools for front-end frameworks
Tools and resources to increase productivity during front-end development
While front-end frameworks like Vue.js, React, and Angular are powerful on their own, their effectiveness can be significantly improved by using complementary tools and resources. These tools help streamline workflows, improve code quality, and speed up the development process. Here's a look at some essential tools that can improve productivity during front-end development.
Code editors and IDEs:
Visual Studio Code (VS Code):
VS Code is a lightweight but powerful code editor that has become the go-to choice for many front-end developers. With an extensive library of extensions, including those specially designed for Vue.js, React, and Angular, it provides features such as syntax highlighting, IntelliSense, debugging, and Git integration, making development faster and more efficient.
Version control systems:
Git: Git is an essential tool for version control in modern development. It allows developers to track changes, collaborate with others, and effectively manage multiple versions of a project. Platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket integrate seamlessly with Git, providing additional features such as issue tracking, pull requests, and continuous integration.
Access a future-proof career in tech with our programs and courses with payment plans spread over 6 months starting at €375/month. Join us now!
Main frameworks in Python
Overview of the main Python frameworks
Python is renowned for its versatility and ease of use, making it a popular choice for back-end development. Among the various frameworks available, Django, Flask, and FastAPI stand out as the most used and respected. Each framework offers unique benefits, meeting the different needs of the project and the preferences of developers. Here's an overview of these main Python frameworks and why you might choose them for your next project.
Django
Django is a comprehensive, top-level web framework that follows the “batteries included” philosophy. It provides everything you need to create complex, database-based websites right from the start.
Why Django?
Comprehensive and feature-rich: Django has a wide range of built-in features, including an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) system, authentication, URL routing, and an administration interface.
Flask
Flask is a micro-framework that offers simplicity and flexibility, making it a favorite for developers who prefer to build applications from scratch. Unlike Django, Flask only provides the essential components needed to run a web application, allowing developers to choose the tools and libraries they need for their specific project.
Why Flask?
Flask is a “micro” framework, which means it doesn't impose dependencies or dictate how your application should be structured. This makes it very flexible, allowing developers to create exactly what they need without overloading them unnecessarily.
FastAPI
FastAPI is a modern and fast (high performance) web framework for creating APIs with Python. It is based on standard Python-like guidelines and is designed to be easy to use while providing high performance, comparable to frameworks like Node.js and Go.
Why choose FastAPI?
Performance: FastAPI relies on Starlette for the web parts and Pydantic for the data parts, making it one of the fastest Python frameworks on the market. It is particularly suitable for projects where performance is a critical factor, such as APIs that require low latency and high throughput.
Automatic documentation: FastAPI automatically generates interactive API documentation using Swagger UI and ReDoc, making it much easier to test and understand API endpoints. This feature is very useful for developers and customers alike, as it improves communication and speeds up the development process.
Advantages and disadvantages of Python frameworks
When choosing a core Python framework, it's critical to weigh the pros and cons of each based on factors such as performance, ease of use, community support, scalability, and flexibility. Here's a detailed comparison of Django, Flask, and FastAPI to help you choose the framework that best fits your needs.
Django
Pros:
Django is a comprehensive framework that includes everything you need to build a web application, from ORM to authentication to an admin interface.
Cons:
Django's “batteries included” approach can be difficult for smaller projects or for developers who want greater flexibility in choosing components.
Flask
Advantages:
Flask is a microframework that provides only the essentials, allowing developers to build applications with minimum overhead and maximum control.
Cons:
Flask's flexibility comes at the cost of fewer built-in tools and features compared to Django. Developers may need to integrate third-party libraries for tasks such as database management, authentication, and form validation.
FastAPI
Advantages:
FastAPI is one of the fastest Python frameworks, thanks to its use of asynchronous programming and the underlying Starlette and Pydantic libraries. It is ideal for applications that require low latency and high throughput.
Cons:
FastAPI is newer than Django and Flask, which means its community and ecosystem continue to grow. This may result in fewer third-party extensions and documentation compared to more established frameworks.
| Framework | Benefits | Disadvantages |
| Django | Full framework with built-in ORM, authentication, and administration interface. | The “batteries included” approach can be challenging for smaller projects or when flexibility is desired. |
| Flask | Micro-framework with minimal overhead, allowing maximum control and customization. | Lack of built-in tools and features, requiring third-party libraries for database management, authentication, etc. |
| Fast API | High performance thanks to asynchronous programming; ideal for low latency and high speed applications. | Newer framework with a growing community, which may result in fewer third party extensions and less comprehensive documentation. |
Specific use cases
Understanding the strengths of Django, Flask, and FastAPI can help you choose the right framework for your project. Below are specific use cases where each Python framework shines, allowing you to take advantage of its unique capabilities in an effective manner.
Django
Use case 1: E-commerce platforms
Why does Django excel? Django's comprehensive set of built-in features, including an ORM, user authentication, and administration interface, makes it ideal for building E-commerce platforms. It provides the tools needed to manage user accounts, product lists, orders, and payment processing, while ensuring security and scalability.
Project example: complete online store with user profiles, shopping carts, order tracking, payment integration, and an admin dashboard for product and user management.
Use case 2: Content Management Systems (CMS)
Why Django excels: Django was originally designed to create content-rich websites, making it perfect for developing CMS applications. Its administration interface allows content managers to easily create, edit, and organize content, while its ORM makes it easy to manage data fluidly.
Project example: a custom CMS for a news website that allows publishers to manage articles, images, and videos, with features to categorize content, schedule posts, and manage user comments.
Flask
Use case 1: microservices and APIs
Why Flask excels: The lightweight and flexible nature of Flask makes it perfect for building RESTful microservices and APIs. Developers can quickly set up endpoints, manage HTTP requests, and integrate databases or other services without unnecessary costs.
Project example: a microservice that manages user authentication for a larger application, by providing JWT-based authentication, user registration, and login/logout functionalities.
Use case 2: single-page applications (SPA)
Why Flask excels: Flask is perfectly suited to serve as a back-end for SPAs, where the front-end is typically built with frameworks like React or Vue.js. Flask can manage the main logic and endpoints of the API, while the front-end takes care of the user interface and interactions.
Project example: a real-time chat application where Flask manages user sessions, message storage, and API endpoints, while the front-end manages the user interface and WebSocket connections for live messaging.
Main PHP Frameworks
Introduction
Laravel, Symfony, CodeIgniter: general overview
PHP is still one of the most used languages for back-end development, especially in web applications. Among the many PHP frameworks available, Laravel, Symfony, and CodeIgniter stand out for their popularity, robustness, and community support. Here is a general overview of these main PHP frameworks:
Laravel
Laravel is one of the most popular PHP frameworks, known for its elegant syntax and developer friendly features. Created by Taylor Otwell in 2011, Laravel quickly became the framework of choice for many developers due to its focus on simplicity, readability, and ease of use.
Features: Laravel offers a rich set of features including an ORM (Eloquent), routing, middleware, authentication, and a powerful model building engine (Blade). It also includes built-in tools for caching, queuing, and task scheduling, making it suitable for building modern, complex web applications.
Use case:
- Content Management Systems (CMS)
- E-commerce platforms
- Social networking sites
- API development
Symfony
Symfony is a mature and powerful PHP framework that focuses on reusable components and a modular architecture. It was first published in 2005 by SensioLabs and has since become the cornerstone of enterprise-level PHP development.
Features: Symfony is known for its flexibility, allowing developers to use only the components they need or to adopt the entire framework. It offers features such as an advanced routing system, form management, dependency injection, and a robust HTTP client.
Use case:
- Business applications
- Complex web applications with high scalability requirements
- Projects that require a high level of customization
- Long-term projects that require extensive support and maintenance
CodeIgniter
CodeIgniter is a lightweight and fast PHP framework that focuses on simplicity and speed. Launched in 2006 by EllisLab, CodeIgniter is known for its small footprint and simple approach, making it a great choice for developers who need a fast and flexible solution.
Features: CodeIgniter offers a simple, no-frills approach to web development, with features such as Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, routing, form validation, and session management. It is designed to be easy to set up and use, requiring minimal configuration and offering a flexible learning curve.
Use case:
- Small and medium sized web applications
- Projects that require rapid development and deployment
- Existing projects that require modern features without significant additional costs
- Simple API and core services
Advantages and disadvantages of PHP frameworks
When choosing a PHP framework for your project, it is essential to consider a variety of factors such as security, scalability, and ease of learning. Below is a comparison of Laravel, Symfony, and CodeIgniter based on these aspects:
Laravel
Benefits:
Laravel provides built-in security features such as SQL injection protection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). The framework also supports hashing and encrypting passwords out of the box, making it a secure choice for web applications.
Cons:
Laravel's rich set of features and abstractions can cause some performance overhead, making it less suitable for applications that require minimum latency and high throughput.
Symfony
Advantages:
Symfony is renowned for the importance it places on security. It includes advanced security features such as role-based access control (RBAC), encrypted cookies, and protection against common web vulnerabilities. Symfony's security component is highly configurable, allowing developers to implement customized security measures as required.
Cons:
Symfony's flexibility and feature set can be overwhelming for beginners or for projects that don't require this level of customization. The learning curve is significant, especially for developers who are new to PHP frameworks.
CodeIgniter
Benefits:
CodeIgniter offers basic security features like XSS filtering and CSRF protection. While it doesn't include as many advanced security features as Laravel or Symfony, it does provide enough tools for developers to implement secure practices.
Cons:
Compared to Laravel and Symfony, CodeIgniter has fewer built-in features, which means developers may need to rely on third-party libraries or custom code for advanced features.
Using PHP frameworks for web development
PHP frameworks like Laravel, Symfony, and CodeIgniter are versatile and powerful tools for creating different types of web applications. Here are some examples of concrete projects that demonstrate the strengths of each framework:
Laravel
Example 1: E-commerce Platforms
- Project: A comprehensive E-commerce website for an online clothing store.
- Description: Laravel is ideal for building E-commerce platforms thanks to its robust features such as Eloquent ORM for database management, built-in authentication for secure user management, and the Blade template engine for creating dynamic and responsive user interfaces. The project may include product lists, shopping cart features, user accounts, payment gateway integration, and an admin panel for order and inventory management.
- Result: The resulting application is secure, scalable, and easy to maintain, with features that improve the user experience and streamline administrative tasks.
Symfony
Example 1: Enterprise Resource Planning System (ERP)
- Project: An ERP system that allows a manufacturing company to manage inventory, orders, production schedules, and finances.
- Description: Symfony's modularity and high level of customization make it an excellent choice for developing complex business applications such as ERP systems. The powerful components of the framework, such as the HTTP client and the form component, can be used to create sophisticated user interface and backend logic. Symfony's support for RESTful APIs also allows for easy integration with other business systems.
- Result: The ERP system is robust, scalable and customizable, which allows the company to optimize its operations and improve the efficiency of the various departments.
Development with Node.js
Introduction to Node.js
Node.js is an open source, cross-platform runtime environment that allows developers to execute Javascript code outside of a web browser. Based on Chrome's V8 Javascript engine, Node.js is designed to build scalable network applications. It was originally released in 2009 by Ryan Dahl and has since become a popular choice for server-side development, thanks to its non-blocking, event-based architecture.
Why use Node.js?
Node.js is based on an asynchronous and non-blocking event-driven architecture. This means that it can process multiple requests simultaneously without waiting for one operation to complete before starting another one. This makes Node.js highly efficient and suitable for creating applications that require high concurrency, such as real-time applications, chat servers, and API services.
Main Node.js frameworks
Node.js provides a powerful environment for creating server-side applications, and various frameworks have been developed to simplify and improve the development process. Express.js and NestJS are two of the most popular and used Node.js frameworks. Here is an overview of each of them:
Express.js
Express.js, commonly referred to simply as Express, is a minimalistic and flexible web application framework for Node.js. It was released in 2010 and has since become one of the most popular frameworks for building web applications and APIs with Node.js.
Features:
Express is lightweight and does not impose a specific structure or set of tools on developers. This makes it very flexible, allowing developers to build their applications as they see fit.
Use case:
- API development: Express is often used to create RESTful APIs because of its simple routing and middleware features.
- Single-page applications (SPAs): Express can serve as the main server for SPAs built with front-end frameworks such as React, Angular, or Vue.js.
Nest JS
NestJS is a progressive Node.js framework for creating efficient, reliable, and scalable server-side applications. It was first published in 2017 by Kamil Myśliwiec and quickly gained popularity thanks to its modular architecture and use of TypeScript. NestJS is built on Express (or possibly Fastify) and uses modern Javascript, heavily inspired by Angular.
Features:
NestJS encourages the use of modules, which allow developers to organize their code into cohesive blocks that can be easily reused and maintained. This modularity is particularly advantageous for large-scale applications.
Use case:
- Enterprise applications: NestJs' modular architecture and TypeScript support make it ideal for creating large-scale enterprise applications that require maintainability and scalability.
- Microservices: NestJS integrates support for microservice architecture, making it easy for developers to create distributed systems.
Using Node.js in Full Stack Applications
Node.js is a versatile platform that excels at creating comprehensive applications thanks to its ability to manage server side and client side development using Javascript. Below are some common use cases for Node.js in Full Stack applications, as well as examples of how it integrates with other technologies to create powerful, scalable, and efficient web applications.
Real-time web applications
Use case:
Node.js is ideal for creating real-time chat applications where users need to exchange messages instantly. The non-blocking, event-driven nature of Node.js makes it ideal for managing numerous simultaneous connections, which is critical for real-time communications.
Integration:
- Socket.io: Node.js integrates seamlessly with Socket.io, a library that allows real-time, bi-directional communication between clients and servers. Socket.io is often used to implement WebSockets, which allow the server to deliver updates to the client in real time.
- Frontend integration: The front-end of a chat application can be created using frameworks such as React, Angular, or Vue.js, while the back-end uses Node.js and Socket.io to manage user sessions, message delivery, and discussion board management.
Example:
A real-time chat platform where users can join discussion forums, send messages, and receive live updates, all powered by Node.js and Socket.io, with a responsive interface built using React.
Single page applications (SPA)
Use case:
SPAs are web applications that load a single HTML page and update content dynamically as the user interacts with the application. Node.js is often used as the main server for SPAs, managing API requests, data retrieval, and user authentication.
Integration:
- Express.js: Node.js, combined with Express.js, is commonly used to create RESTful APIs that serve as a backend for SPAs. These APIs process requests from the front-end and interact with databases to retrieve or update data.
- Front-end integration: SPAs are generally built using front-end frameworks such as Angular, React, or Vue.js. These frameworks manage the user interface and communicate with the Node.js Back End through API calls.
Example: A project management
tool whose user interface is built with React, providing a smooth single-page experience, while the back-end is powered by Node.js and Express.js, managing tasks, projects, and user data through RESTful APIs.
Tools and libraries for Node.js
NPM (Node Package Manager): NPM is the default package manager for Node.js and one of the most essential tools for any Node.js developer. It is a vast repository of open source packages, modules, and libraries that can be easily integrated into your projects. With over 1 million packages available, NPM allows developers to quickly find and integrate solutions to common problems, saving time and effort.
Webpack: Webpack is a powerful module bundler that plays a crucial role in modern Javascript development, including Node.js applications. It takes modules with dependencies and generates static assets representing those modules.
Express.js: Express.js is a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for building web and mobile applications. Express, one of the most popular frameworks for Node.js, simplifies the development process by providing essential tools for routing, middleware, and HTTP management.
PM2: PM2 is a production process manager for Node.js applications that ensures the proper functioning and reliability of your application in production environments. It provides features such as process monitoring, automatic restart in case of failures, load balancing, and simplified management of multiple application instances.
Babel: Babel is a Javascript compiler that allows developers to use the latest ECMAScript features without worrying about browser compatibility or runtime environment. In the context of Node.js, Babel is often used to transpile modern Javascript syntax into a version that is compatible with older environments.
ESLint: ESLint is a static code analysis tool that identifies and reports patterns found in ECMAScript/Javascript code, with the aim of making code more consistent and avoiding bugs.
Morgan: Morgan is a middleware library for Express.js that records HTTP requests. It provides developers with detailed logs of incoming requests, which can be very useful for debugging and tracking the behavior of your application.
Nodemon: Nodemon is a utility that automatically restarts your Node.js application when it detects file changes in the directory. This tool is especially useful during development because it eliminates the need to manually shut down and restart the server every time you change the code.
Passport.js: Passport.js is a popular authentication middleware for Node.js that provides a simple and flexible way to manage authentication in web applications. It supports a wide range of authentication strategies, including username and password, OAuth, and social login providers such as Google, Facebook, and Twitter.
Socket.io: Socket.io is a library that allows for real-time, bi-directional, and event-based communication between web clients and servers. It relies on WebSockets but falls back to other technologies if WebSockets are not supported by the client or server.
Database management
Basic principles of relational databases
Relational databases are a fundamental part of modern web applications. They provide a structured way to store, retrieve, and manage data. Understanding the basics of relational databases, including SQL, data modeling, and standardization, is critical for effective database management and application development.
SQL (structured query language):
What is SQL?
SQL is the standard language used to interact with relational databases. It allows developers to create, read, update, and delete (often referred to as CRUD operations) data stored in a relational database. SQL is also used to define the structure of the database (for example, tables, indexes) and to control access to data.
Key SQL commands:
- SELECT: retrieves data from one or more tables.
- INSERT: Adds new rows of data to a table.
- UPDATE: Changes existing data in a table.
- DELETE: Deletes data from a table.
- CREATE TABLE: Define a new table and its columns.
- ALTER TABLE: Modifies the structure of an existing table.
- DELETE A TABLE: Deletes a table and its data from the database.
- JOIN: combines rows from two or more tables based on an associated column.
SQL is declarative, that is, it specifies what you want to do (for example, retrieve certain rows), and the database management system (DBMS) determines how to do it effectively.
Data modeling:
What is data modeling?
Data modeling is the process of creating a plan that shows how data is stored, organized, and accessed in a database. This involves defining tables, columns, data types, and relationships between the various entities in the database.
Key data modeling concepts:
- Entities and tables: In a relational database, data is organized into tables, with each table representing an entity (for example, customers, orders, products). Each row in a table corresponds to one record and each column corresponds to an attribute of the entity.
- Relationships: relationships define how tables relate to each other. The most common types of relationships include:
- One by one: each record in table A is linked to a record in table B.
- One to many: each record in table A is linked to several records in table B.
- Multiple to multiple: The records in array A are linked to multiple records in array B, and vice versa. This is usually implemented using a junction table.
Example:
Let's imagine an E-commerce database containing tables for customers, orders, and products. A customer can place numerous orders (one-to-many relationship), and an order can include multiple products (many-to-many relationship). Data modeling involves defining these tables, the relationships between them, and the constraints that ensure data integrity.
Choosing a database management system (DBMS)
Choosing the right database management system (DBMS) is a critical decision that can have a significant impact on the performance, scalability, and ease of management of your applications. MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MariaDB are three of the most popular open source relational database systems. Each has strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different use cases. Here is a comparison of their pros and cons:
MySQL
Pros:
MySQL is known for its user-friendly nature, making it a great choice for beginners and experienced developers alike. It has extensive documentation and a large community, which means it's relatively easy to find resources and solutions to problems.
Cons:
Compared to PostgreSQL, MySQL has fewer advanced features, including complex queries, full-text search, and support for non-relational data types.
PostgreSQL
Benefits:
PostgreSQL is known for its rich set of advanced features, including support for complex queries, full-text search, JSON data types, and custom data types. It also supports transactions, making it ideal for applications that require high data integrity.
Cons: PostgreSQL's advanced features and flexibility come with a steeper learning curve, which can be difficult for beginners or developers who are used to simpler systems like MySQL.
Maria DB
Advantages:
MariaDB is a fork of MySQL, created by the original developers of MySQL. It is designed to be fully compatible with MySQL, which means that applications designed for MySQL can generally be run on MariaDB without any changes. This makes it an immediate replacement for MySQL.
Cons:
Although MariaDB is highly compatible with MySQL, its ecosystem is not as large. Some tools and libraries that work with MySQL may not be fully compatible with MariaDB, although that becomes less of an issue over time.
Optimizing relational databases
Optimizing relational databases is critical to improving performance, ensuring efficient data extraction, and maintaining scalability as your application grows. Key optimization techniques include indexing, writing optimized queries, and following best practices in database design and management.
Indexing
What is indexing?
Indexing is a technique used to speed up the retrieval of data from a database table by creating a data structure that allows for faster search operations. An index is similar to a book index; it allows the database to find rows more efficiently without having to go through the entire table.
Index types:
- Primary index: created automatically when a primary key is defined. This ensures that each row in the table can be uniquely identified.
- Secondary index: created on columns other than the primary key to improve query performance. This is useful for columns that are frequently used in WHERE clauses or JOIN operations.
- Composite index: index on several columns. Composite indexes are especially useful when queries filter across multiple columns simultaneously.
Optimized queries
Writing effective queries:
- Select only the columns you need: avoid using SELECT* in your queries. Instead, specify only the columns you need. This reduces the amount of data transferred and processed, improving query performance.
- Use joins effectively: When joining multiple tables, make sure that the join conditions are indexed and that you are joining them on the correct columns. Use INNER JOINS instead of OUTER JOINS when you only need the corresponding rows from both tables.
- Filter early: Use WHERE clauses to filter data as early in your query as possible. This reduces the number of rows that subsequent operations need to process.
- Avoid N+1 query issues: When retrieving associated data, avoid running a separate query for each associated item (N+1 problem). Instead, use JOINs or sub-queries to retrieve all of the data in a single query.
- Use LIMIT for large result sets: if you don't need all rows returned by a query, use the LIMIT clause to limit the number of rows returned. This is especially useful for paginating results.
Query optimization techniques:
- EXPLAIN statements: Use the EXPLAIN statement to analyze how the database executes a query. It shows the query execution plan, including the indexes used, the order of operations, and the estimated number of rows processed. This makes it possible to identify bottlenecks and optimize the query.
- Avoid sub-queries: In some cases, sub-queries may be ineffective. Consider rewriting subqueries as JOINs, especially if the subquery is not selective or returns many rows.
Development with MongoDB
MongoDB is a leading NoSQL database that offers a flexible and scalable solution for managing large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data. Unlike traditional relational databases, MongoDB uses a document-oriented data model, making it ideal for modern web applications that require high performance, flexibility, and the ability to handle a variety of data types. Here's an overview of the core concepts of MongoDB, including NoSQL, document structure, and collection usage.
1. NoSQL databases
What is NoSQL?
NoSQL databases are a category of databases designed to handle a wide variety of data models, including key-value, document, column family, and chart formats. Unlike relational databases that use structured tables and schemas, NoSQL databases offer greater flexibility in data storage and retrieval, making them ideal for applications with large, varied, and dynamic data sets.
NoSQL database types:
- Document-oriented databases: Store data as documents, usually in JSON or BSON format. MongoDB falls into this category.
- Key-value stores: Store data as key-value pairs, useful for caching and session management.
- Stores by column family: Store data in columns instead of rows, ideal for analytic workloads.
- Graphical databases: store data in the form of nodes and edges, suitable for applications involving complex relationships, such as social networks.
Benefits of NoSQL:
- Flexibility: NoSQL databases can store a variety of data types and formats, allowing for rapid iteration and changes to data models without requiring significant schema changes.
- Scalability: NoSQL databases are designed to scale horizontally, making it easy to distribute data across multiple servers and process large-scale, high-traffic applications.
Document structure in MongoDB
What is a document in MongoDB?
In MongoDB, data is stored as documents, which are similar to JSON objects but stored in a binary format called BSON (Binary JSON). Each document is a standalone data entity that contains fields (key-value pairs), and its structure may vary from other documents in the same collection.
Key features of MongoDB documents:
- Dynamic schema: MongoDB allows documents in the same collection to have different fields, types, and structures. This flexibility allows developers to store data in a way that naturally meets application requirements without having to predefine a strict schema.
- Hierarchical data: MongoDB documents can contain nested documents or tables, allowing complex hierarchical data to be represented in a single document.
- Rich data types: MongoDB supports a wide range of data types including strings, numbers, dates, tables, embedded documents, etc. This allows various data to be stored in a single document.
Using collections in MongoDB
What is a collection?
A collection in MongoDB is similar to a table in a relational database. It is a collection of MongoDB documents, and all documents in a collection may have different structures. Collections are flexible and can grow dynamically as new material is added.
Creation and management of collections:
- Creating a collection: collections in MongoDB are created automatically when you insert the first document. However, you can also create a collection explicitly using the db.createCollection () method.
- Inserting documents: You can insert documents into a collection using methods such as insertOne (), insertMany (), or by saving an object directly into the collection. MongoDB does not apply a schema, which allows for flexibility in document structure.
- Querying documents: MongoDB provides powerful query capabilities, allowing you to retrieve documents based on a variety of criteria using methods such as find (), findOne (), and aggregate (). Queries can be filtered, sorted, and restricted to meet specific application needs.
- Index: just like in relational databases, indexes can be created on fields in MongoDB collections to improve query performance. MongoDB supports single-field indexes, compound indexes, and more complex indexing strategies.
- Updating documents: MongoDB supports several update operations, including updateOne (), updateMany (), and replaceOne (). You can update documents partially, change nested fields, or replace entire documents.
- Deleting documents: Documents can be deleted using deleteOne (), deleteMany (), or drop () for entire collections. Delete operations are simple and support criteria-based filtering.
DevOps in Full Stack Development
DevOps Overview
DevOps is a set of practices, tools, and cultural philosophies that aim to bridge the gap between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops). The core idea of DevOps is to enable better collaboration and communication between development and operations teams, thereby increasing the speed, efficiency, and reliability of software delivery. DevOps focuses on automation, continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), monitoring, and feedback loops to ensure that software is designed, tested, and deployed in a consistent and repeatable manner.
Key DevOps principles:
DevOps fosters a culture of collaboration between developers, operational teams, and other stakeholders, breaking traditional silos and encouraging shared responsibilities in the software development lifecycle.
Why DevOps is important in Full Stack Development:
Shorter time to market:
In Full Stack development, where developers manage both front-end and core components, the ability to deliver new features and updates quickly is critical. DevOps practices like CI/CD help speed up release cycles by automating creation, testing, and deployment processes.
Enhanced collaboration and efficiency: Full Stack
developers often work on different parts of the application stack, including the front-end, back-end, and database. DevOps encourages close collaboration between developers, operational teams, and other stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is aligned with goals, processes, and responsibilities.
Key DevOps practices
Continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD), infrastructure as code, monitoring
DevOps focuses on several key practices that enable teams to deliver software more efficiently, reliably, and of higher quality. Three of the most important DevOps practices are continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD), infrastructure as code (IaC), and monitoring.
Continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD)
Continuous integration (CI):
What is CI?
Continuous integration is the practice of frequently integrating code changes into a shared repository, where automated builds and tests are run. The aim of CI is to detect and resolve integration issues at an early stage, ensuring that the code base always remains deployable.
Why CI matters:
In Full Stack development, where multiple developers work on different parts of the application (front-end, back-end, database), CI ensures that changes made by different team members are seamlessly integrated and tested immediately. This prevents integration issues from piling up and becoming more difficult to solve later.
Continuous Deployment (CD):
What is a CD?
Continuous deployment is the process of automatically deploying each code change that passes automated tests in production. This eliminates manual deployment steps, allowing for faster and more frequent releases.
Why the CD is important:
As part of comprehensive development, the CD allows teams to deliver new features, patches, and updates to users quickly and reliably. By automating the deployment process, CD reduces the risk of human error and ensures that updates are deployed consistently across environments.
DevOps tools for Full Stack development
DevOps relies heavily on a variety of tools to automate, manage, and monitor development and deployment processes. These tools help streamline workflows, ensure consistency, and improve collaboration between development and operations teams. Below is an overview of some of the most popular DevOps tools used in Full Stack development, including Docker, Kubernetes, Jenkins, and more.
Docker
What is Docker?
Docker is a platform that allows developers to automate the deployment of applications in lightweight, portable containers. Containers bring together an application and its dependencies, ensuring that it runs consistently across environments.
Functionality:
Docker allows you to group applications and their dependencies, libraries, and configuration files into containers that can be run anywhere: on a developer's laptop, in test environments, or in production.
Kubernetes
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open source platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It orchestrates the operation of containers, ensuring that they are deployed and operate effectively on a cluster of machines.
Features:
Kubernetes automates container deployment and management, managing tasks such as load balancing, scaling, and failover. It ensures the smooth functioning and efficiency of applications.
Integrate DevOps into your workflow
Incorporating DevOps into your development workflow is critical to improving collaboration, improving efficiency, and delivering high-quality software more quickly. To achieve seamless integration, you need to focus on promoting a DevOps culture, automating processes, and using the right tools effectively. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to incorporate DevOps practices into your development process.
Foster a DevOps culture
DevOps starts with breaking down traditional silos between development, operations, and other stakeholders. Encourage open communication and collaboration across teams to ensure everyone is aligned with goals, processes, and responsibilities. Regular meetings, cross-functional meetings, and shared documentation can help everyone stay on the same page.
Web Security in Full Stack Development
Web Security Overview
Web security is an essential aspect of Full Stack development, as it involves protecting both the client side (Front End) and server side (back-end) components of an application from a variety of threats and vulnerabilities. In today's digital landscape, where data breaches and cyberattacks are becoming more common, understanding and addressing the key security challenges associated with web development is critical to protecting sensitive data, protecting user privacy, and maintaining the integrity of your applications. Here's a look at some of the most pressing security challenges in web development.
Cross-site scripting (XSS)
What is XSS?
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a type of security vulnerability that allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. These scripts can then run in the victim's browser, which can lead to the theft of sensitive data, such as cookies, session tokens, or user credentials.
Main challenges:
- User input cleaning: Ensure that all user input is properly cleaned and validated to prevent malicious code from running in the application.
- Output escape: secure display of user-generated content by avoiding special characters that may be interpreted as executable code by the browser.
SQL injection
What is SQL injection?
SQL injection is a code injection technique that allows attackers to manipulate SQL queries by inserting or modifying SQL code via user inputs. This may result in unauthorized access to database content, data modification, or even the deletion of entire databases.
Main challenges:
- Input validation: Ensure that all user inputs are properly validated and cleaned up to prevent attackers from injecting malicious SQL code.
- Parameterized queries: use of parameterized queries or prepared statements to securely pass user input to SQL queries, reducing the risk of SQL code injection.
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
What is the CSRF?
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is an attack that encourages users to perform unintended actions on a web application in which they are authenticated. By exploiting the user's active session, an attacker can execute unauthorized commands, such as changing account settings or completing transactions.
Main challenges:
Implementation of anti-CSRF tokens included in forms and verified by the server to ensure that the request is legitimate and from the user. Configuring cookies with the SameSite attribute to prevent them from being sent with cross-site requests, thus reducing the risk of CSRF attacks.
Security best practices for Full Stack developers
Security is a major concern for Full Stack developers, as web applications are frequently targeted by attackers looking to exploit vulnerabilities. By following best practices, developers can significantly reduce the risk of breaches, protect sensitive data, and ensure the integrity of their applications. Below are some of the most important security practices for Full Stack developers, with an emphasis on securing APIs, managing sessions, and preventing common attacks like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF).
Securing APIs
Use HTTPS: Always
use HTTPS to encrypt data transmitted between the client and the server. This prevents attackers from intercepting sensitive information, such as API keys, user credentials, and personal data. The HTTPS protocol should be applied to all API endpoints.
Authentication and authorization:
- Token-based authentication: Implement token-based authentication methods, such as OAuth 2.0 or JWT (JSON web tokens), to authenticate API requests. Tokens should be stored securely on the client side and transmitted at each request.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Use RBAC to restrict access to API endpoints based on the user's role. Ensure that users can only access resources that they are authorized to interact with.
- API keys: Use API keys to access public APIs, but make sure they are stored securely and refreshed regularly. Avoid hardcoding API keys in client-side code or in version control.
Validation and disinfection of entrances:
- Input validation: Validate all entries to ensure that they comply with the expected formats, types, and ranges. Reject any malformed or unexpected entries.
- Sanitation: Sanitize user input to remove or neutralize potentially dangerous content prior to treatment. This helps prevent injection attacks, such as SQL injection or command injection.
2. Managing sessions
Secure session cookies:
- HttpOnly: Set the HttpOnly attribute on session cookies to prevent client-side scripts from accessing them. This reduces the risk of XSS attacks.
- Secure: Set the Secure attribute on cookies to ensure that they are only transmitted via HTTPS. This prevents attackers from intercepting cookies in transit.
- SameSite: Use the SameSite attribute to restrict how cookies are sent during cross-site requests, reducing the risk of CSRF attacks.
Session expiration and invalidation:
- Session timeout: Implement session timeout policies to automatically log users out after a period of inactivity. This reduces the risk of session hijacking.
- Session invalidation: Invalidates sessions when users sign out or change sensitive account settings (for example, passwords). Ensure that all active sessions associated with the user have ended.
Tools and techniques for securing web applications
Securing web applications is an ongoing process that involves both proactive and reactive measures. Full Stack developers need to use a combination of tools and techniques to identify vulnerabilities, prevent security breaches, and ensure that applications are resilient to attacks. Below is an overview of essential tools and techniques for securing web applications, with an emphasis on vulnerability analysis tools and secure development practices.
Vulnerability analysis tools
What are vulnerability analysis tools?
Vulnerability analysis tools are automated software solutions that scan web applications, servers, and networks to identify security vulnerabilities. These tools help developers detect weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers, such as outdated software, misconfigurations, and insecure code practices.
Main vulnerability analysis tools:
OWASP ZAP (Proxy Zed Attack):
OWASP ZAP is an open source web application security scanner managed by the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP). It is designed to detect vulnerabilities in web applications, such as SQL injection, XSS, and CSRF.
Features: ZAP includes automated scanners, a variety of tools for manual testing, and a powerful REST API. It is suitable for developers as well as security professionals.
Use case: Use ZAP to conduct regular security scans of your web applications during development and prior to deployment. This is especially useful for identifying common vulnerabilities in real time as you develop.
Burp suite:
Burp Suite is a powerful web vulnerability scanner and penetration testing toolkit. It includes features for analyzing web applications, intercepting traffic, and testing various types of vulnerabilities.
Features: Burp Suite offers automated and manual testing capabilities, including vulnerability analysis, fuzzing, and advanced attack simulations.
Nikto:
Nikto is an open source web server scanner that identifies potential issues on web servers, including outdated software, insecure files, and configuration errors.
Features: Nikto analyzes over 6,700 potentially dangerous files and programs, searches for outdated versions of over 1,250 servers, and for version-specific issues on over 270 servers.
Securing web applications requires a combination of effective tools and rigorous development practices. By using vulnerability analysis tools like OWASP ZAP, Nessus, and Burp Suite, Full Stack developers can identify and address potential security issues early in the development process. Adhering to secure coding guidelines, such as input validation, output coding, and appropriate session management, further enhances application security. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and ongoing monitoring ensure that your application is secure over time. By integrating these tools and techniques into your workflow, you can create and manage robust and secure web applications that protect both your users and your data.